TREM-1 promotes survival during Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in mice
- PMID: 24396044
- PMCID: PMC3957993
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01347-13
TREM-1 promotes survival during Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in mice
Abstract
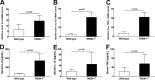
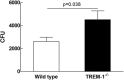
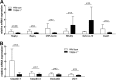
Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess (KPLA) is prevalent in East Asia. Liver abscess can develop after translocation of K. pneumoniae from a patient's bowel into the liver via the portal circulation. TREM-1 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1) amplifies inflammatory signaling during infection, but its role in KPLA is poorly understood. We used an animal study to characterize the role of TREM-1 in KPLA. We compared survival rates, bacterial burdens in tissues, inflammatory cytokine levels, and histology findings between wild-type and Trem-1 knockout (KO) mice after oral inoculation of capsular type K1 K. pneumoniae. Translocation of K. pneumoniae to mesenteric lymph nodes and liver was examined, and intestinal permeability, antimicrobial peptide expression, and the clearance of K. pneumoniae in the small intestine were determined. In the absence of TREM-1, KPLA model mice showed increased K. pneumoniae dissemination, enhanced liver and systemic inflammation, and reduced survival. Impaired bacterial clearance in the small intestine causes enhanced K. pneumoniae translocation, which renders Trem-1 KO mice more susceptible to K. pneumoniae oral infection. In conclusion, TREM-1-mediated bacterial clearance in the small intestine is an important immune response against K. pneumoniae. TREM-1 deficiency enhances K. pneumoniae translocation in the small intestine and increases mortality rates in mice with KPLA.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1/3 in Klebsiella-derived pneumosepsis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Nov;53(5):647-55. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0485OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25860078
-
Ampicillin and amoxicillin use and the risk of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in Taiwan.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jul 15;208(2):211-7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit157. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23568176
-
Do neutrophils play a role in establishing liver abscesses and distant metastases caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae?PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e15005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015005. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21151499 Free PMC article.
-
[Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 as an inflammation amplifier].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2009 Aug;32(4):242-8. doi: 10.2177/jsci.32.242. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2009. PMID: 19721344 Review. Japanese.
-
TREM and TREM-like receptors in inflammation and disease.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Feb;21(1):38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Feb 21. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19230638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Computational Model of Symptomatic Bacteremia to Inform Bacterial Separation Treatment Requirements.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0163167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163167. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27657881 Free PMC article.
-
Excessive Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 18;11:2063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02063. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013872 Free PMC article.
-
Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 Agonist Regulates Intestinal Inflammation via Cd177+ Neutrophils.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 9;12:650864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650864. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33767714 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella effector SpvB aggravates dysregulation of systemic iron metabolism via modulating the hepcidin-ferroportin axis.Gut Microbes. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1-18. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1849996. Gut Microbes. 2021. PMID: 33475464 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Dendritic Cell Maturation, TLR, and TREM1 Signaling Pathways in the Brucella canis Infected Canine Macrophage Cells, DH82, Through Transcriptomic Analysis.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Mar 19;8:619759. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.619759. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33829052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin YT, Chen TL, Siu L, Hsu SF, Fung CP. 2010. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of community-acquired thoracic empyema or complicated parapneumonic effusion caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 29:1003–1010. 10.1007/s10096-010-0961-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

