Rapid isolation of cancer cells using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement structure
- PMID: 24396522
- PMCID: PMC3555967
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4774308
Rapid isolation of cancer cells using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement structure
Abstract
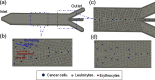
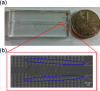
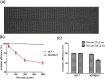
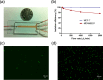
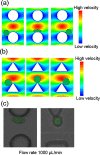
This work reports a microfluidic device with deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) arrays allowing rapid and label-free cancer cell separation and enrichment from diluted peripheral whole blood, by exploiting the size-dependent hydrodynamic forces. Experiment data and theoretical simulation are presented to evaluate the isolation efficiency of various types of cancer cells in the microfluidic DLD structure. We also demonstrated the use of both circular and triangular post arrays for cancer cell separation in cell solution and blood samples. The device was able to achieve high cancer cell isolation efficiency and enrichment factor with our optimized design. Therefore, this platform with DLD structure shows great potential on fundamental and clinical studies of circulating tumor cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cascaded filter deterministic lateral displacement microchips for isolation and molecular analysis of circulating tumor cells and fusion cells.Lab Chip. 2021 Aug 7;21(15):2881-2891. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00360g. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 34219135
-
Topology optimization based deterministic lateral displacement array design for cell separation.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Aug 30;1679:463384. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463384. Epub 2022 Jul 28. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 35940060
-
A Review on Deterministic Lateral Displacement for Particle Separation and Detection.Nanomicro Lett. 2019 Sep 17;11(1):77. doi: 10.1007/s40820-019-0308-7. Nanomicro Lett. 2019. PMID: 34138050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double spiral microchannel for label-free tumor cell separation and enrichment.Lab Chip. 2012 Oct 21;12(20):3952-60. doi: 10.1039/c2lc40679a. Lab Chip. 2012. PMID: 22868446
-
Label-Free and Rapid Microfluidic Design Rules for Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment and Isolation: A Review and Simulation Analysis.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 11;10(7):6306-6322. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08606. eCollection 2025 Feb 25. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40028152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic chip combined with magnetic-activated cell sorting technology for tumor antigen-independent sorting of circulating hepatocellular carcinoma cells.PeerJ. 2019 Apr 1;7:e6681. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6681. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30972256 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of large circulating tumor cells isolated with ultra-high throughput microfluidic Vortex technology.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 15;7(11):12748-60. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7220. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26863573 Free PMC article.
-
Charge-Based Separation of Micro- and Nanoparticles.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Nov 18;11(11):1014. doi: 10.3390/mi11111014. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33218201 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress of Microfluidics in Translational Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016 Apr 20;5(8):871-88. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600009. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016. PMID: 27091777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A micropillar array-based microfluidic chip for label-free separation of circulating tumor cells: The best micropillar geometry?J Adv Res. 2023 May;47:105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.005. Epub 2022 Aug 11. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 35964874 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
