Stroke epidemiology and stroke care services in India
- PMID: 24396806
- PMCID: PMC3859004
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2013.15.3.128
Stroke epidemiology and stroke care services in India
Abstract
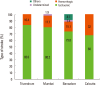
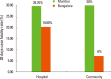
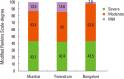
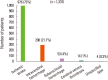
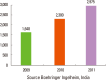
Developing countries like India are facing a double burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases. Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability in India. The estimated adjusted prevalence rate of stroke range, 84-262/100,000 in rural and 334-424/100,000 in urban areas. The incidence rate is 119-145/100,000 based on the recent population based studies. There is also a wide variation in case fatality rates with the highest being 42% in Kolkata. Stroke units are predominantly available in urban areas that too in private hospitals. Intravenous (IV) and intra-arterial thrombolysis (IA) are commonly used in India. In the on-going Indo USA National stroke registry the rate of IV thrombolysis is 11%. Stroke rehabilitation is not well developed in India due to lack of personnel. Organised rehabilitation services are available in the country but they are mainly in private hospitals of the cities. Even though India is a leading generic drugs producer still many people can't afford the commonly used secondary prevention drugs. As a first step the Government of India has started the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS). The government is focusing on early diagnosis, management, infrastructure, public awareness and capacity building at different levels of health care for all the non-communicable diseases including stroke. An organised effort from both the government and the private sector is needed to tackle the stroke epidemic in India.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Incidence; India; Rehabilitation; Stroke; Stroke unit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bonita R, Beaglehole R. Stroke prevention in poor countries. Time for action. Stroke. 2007;38:2871–2872. - PubMed
-
- Pandian JD, Srikanth V, Read SJ, Thrift AG. Poverty and stroke in India. A time to act. Stroke. 2007;38:3063–3069. - PubMed
-
- Abraham J, Rao PS, Inbaraj SG, Shetty G, Jose CJ. An epidemiological study of hemiplegia due to stroke in South India. Stroke. 1970;1:477–481. - PubMed
-
- Bansal BC, Prakash C, Jain AL, Brahmanandam KR. Cerebro-vascular disease in young individuals below the age of 40 years. Neurol India. 1973;21:11–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

