MicroRNAs synergistically regulate milk fat synthesis in mammary gland epithelial cells of dairy goats
- PMID: 24397207
- PMCID: PMC8750411
- DOI: 10.3727/105221613x13776146743262
MicroRNAs synergistically regulate milk fat synthesis in mammary gland epithelial cells of dairy goats
Abstract
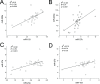
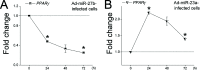
Synergistic regulation among microRNAs (miRNAs) is important to understand the mechanisms underlying the complex molecular regulatory networks in goats. Goat milk fat synthesis is driven by a gene network that involves many biological processes in the mammary gland. These biological processes are affected by several miRNAs rather than a single miRNA. Therefore, identifying synergistic miRNAs is necessary to further understand the functions of miRNAs and the metabolism of goat milk fat synthesis. Using qRT-PCR, we assessed the expression of 11 miRNAs that have the potential to regulate milk fat synthesis in the goat mammary gland. Six of these miRNAs exhibited expression during the lactation cycle. Additionally, we also found that prolactin, the key hormone that regulates lactation, promotes the expression of four miRNAs (miR-23a, miR-27b, miR-103, and miR-200a). Further functional analysis showed that overexpression of all four miRNAs by using recombinant adenovirus in goat mammary gland epithelial cells can affect gene mRNA expression associated with milk fat synthesis. Specifically, elevated miR-200a expression suppressed the mRNA expression of genes involved in fat droplet formation. To analyze the synergistic regulation among these four miRNAs (miR-23a, miR-27b, miR-103, and miR-200a), we used the Pearson correlation coefficient to evaluate the correlation between their expression levels in 30 lactating goats. As a result, we found a strong correlation and mutual regulation between three miRNA pairs (miR-23a and miR-27b, miR-103 and miR-200a, miR-27b and miR-200a). This study provides the first experimental evidence that miRNA expression is synergistically regulated in the goat mammary gland and has identified the potential biological role of miRNAs in goat milk fat synthesis. The identification of synergistic miRNAs is a crucial step for further understanding the molecular network of milk fat synthesis at a system-wide level.
Figures



References
-
- Heinlein GFW, Caccse R. Goat milk versus cow milk. Dairy Goat J 2003; 81:12–14.
-
- Jenness R. Composition and characteristics of goat milk: Review 1968–1979. J Dairy Sci 1980; 63:1605–1630.
-
- Haenlein GFW. Past, present, and future perspectives of small ruminant research. J Dairy Sci 2001; 84:2097–2115. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004; 431:350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
