A joint analysis to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance in three European sheep populations
- PMID: 24397290
- PMCID: PMC4258091
- DOI: 10.1111/jbg.12071
A joint analysis to identify loci underlying variation in nematode resistance in three European sheep populations
Abstract
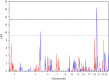
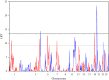
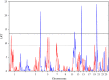
Gastrointestinal nematode infections are one of the main health/economic issues in sheep industries, worldwide. Indicator traits for resistance such as faecal egg count (FEC) are commonly used in genomic studies; however, published results are inconsistent among breeds. Meta (or joint)-analysis is a tool for aggregating information from multiple independent studies. The aim of this study was to identify loci underlying variation in FEC, as an indicator of nematode resistance, in a joint analysis using data from three populations (Scottish Blackface, Sarda × Lacaune and Martinik Black-Belly × Romane), genotyped with the ovine 50k SNP chip. The trait analysed was the average animal effect for Strongyles and Nematodirus FEC data. Analyses were performed with regional heritability mapping (RHM), fitting polygenic effects with either the whole genomic relationship matrix or matrices excluding the chromosome being interrogated. Across-population genomic covariances were set to zero. After quality control, 4123 animals and 38 991 SNPs were available for the analysis. RHM identified genome-wide significant regions on OAR4, 12, 14, 19 and 20, with the latter being the most significant. The OAR20 region is close to the major histocompatibility complex, which has often been proposed as a functional candidate for nematode resistance. This region was significant only in the Sarda × Lacaune population. Several other regions, on OAR1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 12, 19, 20 and 24, were significant at the suggestive level.
Keywords: Joint analysis; SNP; nematode resistance; regional heritability mapping; sheep.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics Published by Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Figures

References
-
- Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J, Nierras C, Plagnol V, Pociot F, Schuilenburg H, Smyth DJ, Stevens H, Todd JA, Walker NM, Rich SS Type 1 Diabet Genetics Consortium. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:703–707. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beh KJ, Hulme DJ, Callaghan MJ, Leish Z, Lenane I, Windon RG, Maddox JF. A genome scan for quantitative trait loci affecting resistance to Trichostrongylus colubriformis in sheep. Anim. Genet. 2002;33:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Behnke JM, Iraqi F, Menge D, Baker RL, Gibson J, Wakelin D. Chasing the genes that control resistance to gastrointestinal nematodes. J. Helminthol. 2003;77:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y, Blank RB, Suffia I. Natural regulatory T cells and parasites: a common quest for host homeostasis. Immunol. Rev. 2006;212:287–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

