Thoracic surface temperature rhythms as circadian biomarkers for cancer chronotherapy
- PMID: 24397341
- PMCID: PMC4221267
- DOI: 10.3109/07420528.2013.864301
Thoracic surface temperature rhythms as circadian biomarkers for cancer chronotherapy
Abstract
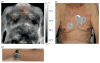
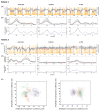
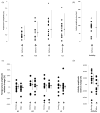
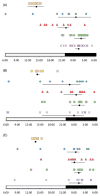
The disruption of the temperature circadian rhythm has been associated with cancer progression, while its amplification resulted in cancer inhibition in experimental tumor models. The current study investigated the relevance of skin surface temperature rhythms as biomarkers of the Circadian Timing System (CTS) in order to optimize chronotherapy timing in individual cancer patients. Baseline skin surface temperature at four sites and wrist accelerations were measured every minute for 4 days in 16 patients with metastatic gastro-intestinal cancer before chronotherapy administration. Temperature and rest-activity were recorded, respectively, with wireless skin surface temperature patches (Respironics, Phillips) and an actigraph (Ambulatory Monitoring). Both variables were further monitored in 10 of these patients during and after a 4-day course of a fixed chronotherapy protocol. Collected at baseline, during and after therapy longitudinal data sets were processed using Fast Fourier Transform Cosinor and Linear Discriminant Analyses methods. A circadian rhythm was statistically validated with a period of 24 h (p < 0.05) for 49/61 temperature time series (80.3%), and 15/16 rest-activity patterns (93.7%) at baseline. However, individual circadian amplitudes varied from 0.04 °C to 2.86 °C for skin surface temperature (median, 0.72 °C), and from 16.6 to 146.1 acc/min for rest-activity (median, 88.9 acc/min). Thirty-nine pairs of baseline temperature and rest-activity time series (75%) were correlated (r > |0.7|; p < 0.05). Individual circadian acrophases at baseline were scattered from 15:18 to 6:05 for skin surface temperature, and from 12:19 to 15:18 for rest-activity, with respective median values of 01:10 (25-75% quartiles, 22:35-3:07) and 14:12 (13:14-14:31). The circadian patterns in skin surface temperature and rest-activity persisted or were amplified during and after fixed chronotherapy delivery for 5/10 patients. In contrast, transient or sustained disruption of these biomarkers was found for the five other patients, as indicated by the lack of any statistically significant dominant period in the circadian range. No consistent correlation (r < |0.7|, p ≥ 0.05) was found between paired rest-activity and temperature time series during fixed chronotherapy delivery. In conclusion, large inter-patient differences in circadian amplitudes and acrophases of skin surface temperature were demonstrated for the first time in cancer patients, despite rather similar rest-activity acrophases. The patient-dependent coupling between both CTS biomarkers, and its possible alteration on a fixed chronotherapy protocol, support the concept of personalized cancer chronotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. Support for this project was provided by ARTBC International and Braun France.
Figures
References
-
- Ahowesso C, Li XM, Zampera S, et al. Sex and dosing-time dependencies in irinotecan-induced circadian disruption. Chronobiol Int. 2011;28:458–70. - PubMed
-
- Bouchahda M, Adam R, Giacchetti S, et al. Rescue chemotherapy using multidrug chronomodulated hepatic arterial infusion for patients with heavily pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:4990–9. - PubMed
-
- Bouchahda M, Macarulla T, Liedo G, et al. Feasibility of cetuximab given with a simplified schedule every 2 weeks in advanced colorectal cancer: A multicenter, retrospective analysis. Med Oncol. 2011;28:S253–8. - PubMed
-
- Bouchahda M, Macarulla T, Spano JP, et al. Cetuximab efficacy and safety in a retrospective cohort of elderly patients with heavily pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;67:255–62. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau P, Shechter A, Dittmar A, et al. Cerebral temperature varies across circadian phases in humans. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008;2008:4856–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
