Correlates and outcomes of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in HIV-exposed uninfected infants
- PMID: 24397463
- PMCID: PMC3897882
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2393-14-7
Correlates and outcomes of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in HIV-exposed uninfected infants
Abstract
Background: Preterm birth (PTB), low birth weight (LBW) and small for gestational age (SGA) contribute to neonatal mortality. Maternal HIV-1 infection has been associated with an increased risk of PTB, but mechanisms underlying this association are undefined. We describe correlates and outcomes of PTB, LBW, and SGA in HIV-exposed uninfected infants.
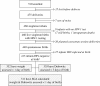
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of cohort study. Between 1999-2002, pregnant, HIV-infected women were enrolled into an HIV-1 transmission study. Logistic regression was used to identify correlates of PTB, LBW and SGA in HIV-negative, spontaneous singleton deliveries. Associations between birth outcomes and mortality were measured using survival analyses.
Results: In multivariable models, maternal plasma (OR = 2.1, 95% CI = 1.1-3.8) and cervical HIV-1 RNA levels (OR = 1.6, 95% CI = 1.1-2.4), and CD4 < 15% (OR = 2.4, 95% CI = 1.0-5.6) were associated with increased odds of PTB. Abnormal vaginal discharge and cervical polymorphonuclear leukocytes were also associated with PTB. Cervical HIV-1 RNA level (OR = 2.4, 95% CI = 1.5-6.7) was associated with an increased odds of LBW, while increasing parity (OR = 0.46, 95% CI = 0.24-0.88) was associated with reduced odds. Higher maternal body mass index (OR = 0.75, 95% CI = 0.61-0.92) was associated with a reduced odds of SGA, while bacterial vaginosis was associated with >3-fold increased odds (OR = 3.2, 95% CI = 1.4-7.4). PTB, LBW, and SGA were each associated with a >6-fold increased risk of neonatal death, and a >2-fold increased rate of infant mortality within the first year.
Conclusions: Maternal plasma and cervical HIV-1 RNA load, and genital infections may be important risk factors for PTB in HIV-exposed uninfected infants. PTB, LBW, and SGA are associated with increased neonatal and infant mortality in HIV-exposed uninfected infants.
Figures
References
-
- Blencowe H, Cousens S, Oestergaard MZ, Chou D, Moller AB, Narwal R, Adler A, Vera Garcia C, Rohde S, Say L. et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the year 2010 with time trends since 1990 for selected countries: a systematic analysis and implications. Lancet. 2012;379(9832):2162–2172. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60820-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials