EmrA1 membrane fusion protein of Francisella tularensis LVS is required for resistance to oxidative stress, intramacrophage survival and virulence in mice
- PMID: 24397487
- PMCID: PMC4097035
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12509
EmrA1 membrane fusion protein of Francisella tularensis LVS is required for resistance to oxidative stress, intramacrophage survival and virulence in mice
Abstract
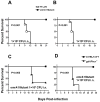
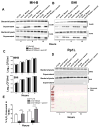
Francisella tularensis is a category A biodefence agent that causes a fatal human disease known as tularaemia. The pathogenicity of F. tularensis depends on its ability to persist inside host immune cells primarily by resisting an attack from host-generated reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS). Based on the ability of F. tularensis to resist high ROS/RNS levels, we have hypothesized that additional unknown factors act in conjunction with known antioxidant defences to render ROS resistance. By screening a transposon insertion library of F. tularensis LVS in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, we have identified an oxidant-sensitive mutant in putative EmrA1 (FTL_0687) secretion protein. The results demonstrate that the emrA1 mutant is highly sensitive to oxidants and several antimicrobial agents, and exhibits diminished intramacrophage growth that can be restored to wild-type F. tularensis LVS levels by either transcomplementation, inhibition of ROS generation or infection in NADPH oxidase deficient (gp91Phox(-/-)) macrophages. The emrA1 mutant is attenuated for virulence, which is restored by infection in gp91Phox(-/-) mice. Further, EmrA1 contributes to oxidative stress resistance by affecting secretion of Francisella antioxidant enzymes SodB and KatG. This study exposes unique links between transporter activity and the antioxidant defence mechanisms of F. tularensis.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Federal Register. Biennial review, Final rule. 194. Vol. 77. Federal Register; 2012. Possession, use and transfer of select agents and toxins; pp. 10–5. - PubMed
-
- Allen LA. Mechanisms of pathogenesis: evasion of killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Microbes Infect. 2003;5:1329–1335. - PubMed
-
- Allen LA, McCaffrey RL. To activate or not to activate: distinct strategies used by Helicobacter pylori and Francisella tularensis to modulate the NADPH oxidase and survive in human neutrophils. Immunol Rev. 2007;219:103–117. - PubMed
-
- Atkins HS, Dassa E, Walker NJ, Griffin KF, Harland DN, Taylor RR, et al. The identification and evaluation of ATP binding cassette systems in the intracellular bacterium Francisella tularensis. Res Microbiol. 2006;157:593–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

