Rational design of a structural framework with potential use to develop chemical reagents that target and modulate multiple facets of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24397771
- PMCID: PMC4096303
- DOI: 10.1021/ja409801p
Rational design of a structural framework with potential use to develop chemical reagents that target and modulate multiple facets of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
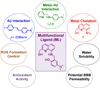
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by multiple, intertwined pathological features, including amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, metal ion dyshomeostasis, and oxidative stress. We report a novel compound (ML) prototype of a rationally designed molecule obtained by integrating structural elements for Aβ aggregation control, metal chelation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulation, and antioxidant activity within a single molecule. Chemical, biochemical, ion mobility mass spectrometric, and NMR studies indicate that the compound ML targets metal-free and metal-bound Aβ (metal-Aβ) species, suppresses Aβ aggregation in vitro, and diminishes toxicity induced by Aβ and metal-treated Aβ in living cells. Comparison of ML to its structural moieties (i.e., 4-(dimethylamino)phenol (DAP) and (8-aminoquinolin-2-yl)methanol (1)) for reactivity with Aβ and metal-Aβ suggests the synergy of incorporating structural components for both metal chelation and Aβ interaction. Moreover, ML is water-soluble and potentially brain permeable, as well as regulates the formation and presence of free radicals. Overall, we demonstrate that a rational structure-based design strategy can generate a small molecule that can target and modulate multiple factors, providing a new tool to uncover and address AD complexity.
Figures



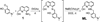
References
-
- Thies W, Bleiler L. Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Dementia. 2013;9:208–245. - PubMed
-
- Corbett A, Pickett J, Burns A, Corcoran J, Dunnett SB, Edison P, Hagan JJ, Holmes C, Jones E, Katona C, Kearns I, Kehoe P, Mudher A, Passmore A, Shepherd N, Walsh F, Ballard C. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012;11:833–846. - PubMed
-
- Jakob-Roetne R, Jacobsen H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:3030–3059. - PubMed
-
- Hamley IW. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:5147–5192. - PubMed
-
- Kepp KP. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:5193–5239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

