Iron chelation and multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 24397846
- PMCID: PMC3906635
- DOI: 10.1042/AN20130037
Iron chelation and multiple sclerosis
Abstract
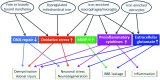
Histochemical and MRI studies have demonstrated that MS (multiple sclerosis) patients have abnormal deposition of iron in both gray and white matter structures. Data is emerging indicating that this iron could partake in pathogenesis by various mechanisms, e.g., promoting the production of reactive oxygen species and enhancing the production of proinflammatory cytokines. Iron chelation therapy could be a viable strategy to block iron-related pathological events or it can confer cellular protection by stabilizing hypoxia inducible factor 1α, a transcription factor that normally responds to hypoxic conditions. Iron chelation has been shown to protect against disease progression and/or limit iron accumulation in some neurological disorders or their experimental models. Data from studies that administered a chelator to animals with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a model of MS, support the rationale for examining this treatment approach in MS. Preliminary clinical studies have been performed in MS patients using deferoxamine. Although some side effects were observed, the large majority of patients were able to tolerate the arduous administration regimen, i.e., 6-8 h of subcutaneous infusion, and all side effects resolved upon discontinuation of treatment. Importantly, these preliminary studies did not identify a disqualifying event for this experimental approach. More recently developed chelators, deferasirox and deferiprone, are more desirable for possible use in MS given their oral administration, and importantly, deferiprone can cross the blood-brain barrier. However, experiences from other conditions indicate that the potential for adverse events during chelation therapy necessitates close patient monitoring and a carefully considered administration regimen.
Figures
References
-
- Adams CW. A Color Atlas of Multiple Sclerosis and Other Myelin Disorders. Dobbs Ferry, NY: Sheridan House Inc; 1989.
-
- Al-Radaideh AM, Wharton SJ, Lim SY, Tench CR, Morgan PS, Bowtell RW, Constantinescu CS, Gowland PA. Increased iron accumulation occurs in the earliest stages of demyelinating disease: an ultra-high field susceptibility mapping study in Clinically Isolated Syndrome. Mult Scler. 2013;19:896–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical