Comparison of pesticide residues in surface water and ground water of agriculture intensive areas
- PMID: 24398360
- PMCID: PMC3895686
- DOI: 10.1186/2052-336X-12-11
Comparison of pesticide residues in surface water and ground water of agriculture intensive areas
Abstract
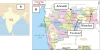
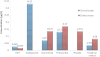
The organochlorines (OClPs) and organophosphates (OPPs) pesticides in surface and ground water having intensive agriculture activity were investigated to evaluate their potential pollution and risks on human health. As per USEPA 8081 B method, liquid-liquid extraction followed by Gas-Chromatographic technique with electron capture detector and mass selective detector (GC-MS) were used for monitoring of pesticides. Among organochlorines, α,β,γ,δ HCH's, aldrin, dicofol, DDT and its derivatives, α,β endosulphan's and endosulphan-sulphate were analysed; dichlorovos, ethion, parathion-methyl, phorate, chlorpyrifos and profenofos were determined among organophosphates.As compared to ground water, higher concentrations of OClPs and OPPs were found in surface water. Throughout the monitoring study, α - HCH (0.39 μg/L in Amravati region),α - endosulphan (0.78 μg/L in Yavatmal region), chlorpyrifos (0.25 μg/L in Bhandara region) and parathion-methyl (0.09 μg/L in Amravati region) are frequently found pesticide in ground water, whereas α,β,γ-HCH (0.39 μg/L in Amravati region), α,β - endosulphan (0.42 μg/L in Amravati region), dichlorovos (0.25 μg/L in Yavatmal region), parathion-methyl (0.42 μg/L in Bhandara region), phorate (0.33 μg/L in Yavatmal region) were found in surface water.Surface water was found to be more contaminated than ground water with more number of and more concentrated pesticides. Among pesticides water samples are found to be more contaminated by organophosphate than organochlorine. Pesticides in the surface water samples from Bhandara and Yavatmal region exceeded the EU (European Union) limit of 1.0 μg/L (sum of pesticide levels in surface water) but were within the WHO guidelines for individual pesticides.
Figures



References
-
- Forget G. In: Impact of Pesticide Use on Health in Developing Countries. Forget G, Goodman T, De Villiers A, editor. Ottawa: IDRC; 1993. Balancing the need for pesticides with the risk to human health; p. 2.
-
- Karunakaran CO. The Kerala food poisoning. J Indian Med Assoc. 1958;31:20. - PubMed
-
- Hundal BS. Anand, Ramandeep Singh. Pesticide Marketing: The Indian Scenario. IUP J Manag Econ. 2006;4:32–37.
-
- Kole RK, Bagchi MM. Pesticide residues in the aquatic environment and their possible ecological hazards. J Inland Fish Soci Ind. 1995;27:79–89.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

