Chemo-informatic strategy for imaging mass spectrometry-based hyperspectral profiling of lipid signatures in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 24398526
- PMCID: PMC3903245
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1310524111
Chemo-informatic strategy for imaging mass spectrometry-based hyperspectral profiling of lipid signatures in colorectal cancer
Abstract
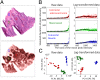
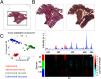
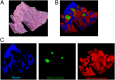
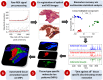
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) provides the opportunity to investigate tumor biology from an entirely novel biochemical perspective and could lead to the identification of a new pool of cancer biomarkers. Effective clinical translation of histology-driven MSI in systems oncology requires precise colocalization of morphological and biochemical features as well as advanced methods for data treatment and interrogation. Currently proposed MSI workflows are subject to several limitations, including nonoptimized raw data preprocessing, imprecise image coregistration, and limited pattern recognition capabilities. Here we outline a comprehensive strategy for histology-driven MSI, using desorption electrospray ionization that covers (i) optimized data preprocessing for improved information recovery; (ii) precise image coregistration; and (iii) efficient extraction of tissue-specific molecular ion signatures for enhanced biochemical distinction of different tissue types. The proposed workflow has been used to investigate region-specific lipid signatures in colorectal cancer tissue. Unique lipid patterns were observed using this approach according to tissue type, and a tissue recognition system using multivariate molecular ion patterns allowed highly accurate (>98%) identification of pixels according to morphology (cancer, healthy mucosa, smooth muscle, and microvasculature). This strategy offers unique insights into tumor microenvironmental biochemistry and should facilitate compilation of a large-scale tissue morphology-specific MSI spectral database with which to pursue next-generation, fully automated histological approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chaurand P, Schwartz SA, Caprioli RM. Imaging mass spectrometry: A new tool to investigate the spatial organization of peptides and proteins in mammalian tissue sections. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6(5):676–681. - PubMed
-
- Chaurand P, Caprioli RM. Direct profiling and imaging of peptides and proteins from mammalian cells and tissue sections by mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis. 2002;23(18):3125–3135. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell RL, Caprioli RM. Tissue profiling by mass spectrometry: A review of methodology and applications. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2005;4(4):394–401. - PubMed
-
- Mirnezami R, et al. Implementation of molecular phenotyping approaches in the personalized surgical patient journey. Ann Surg. 2012;255(5):881–889. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson JK, et al. Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature. 2012;491(7424):384–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

