Extrapyramidal syndrome
- PMID: 24398867
- PMCID: PMC3903097
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009752
Extrapyramidal syndrome
Abstract
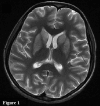
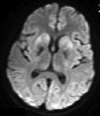
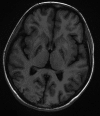
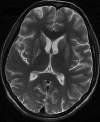
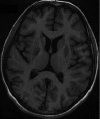
Organophosphate (OP) poisoning is a common occurrence in the rural areas of developing countries like India. Acute cholinergic crisis is one of the important causes of mortality related to OP poisoning. Delayed peripheral neuropathy, extrapyramidal syndromes and neuropsychiatric manifestations are the major consequences of secondary neuronal damage. This case illustrates a 14-year-old girl who ingested 50 mL of OP pesticide and developed extrapyramidal symptoms in the form of parkinsonism and hand dystonia in spite of immediate medical attention. MRI of the brain with T2, fluid attenuated inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted sequences revealed bilateral symmetrical basal ganglia hyperintensities. Further follow-up revealed a significant clinical improvement with marked resolutions of the brain lesions. The reversible extrapyramidal symptoms with disappearance of neuroimaging findings without neuropathy or neuropsychiatric manifestations are unusual in OP poisoning.
Figures
References
-
- Jeyaratnam J. Acute pesticide poisoning: a major global health problem. World Health Stat Q 1990;43:139–44 - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. Organophosphate-induced brain damage: mechanisms, neuropsychiatric and neurological consequences, and potential therapeutic strategies. Neurotoxicology 2012;33:391–400 - PubMed
-
- Hsieh BH, Deng JF, Ger J, et al. Acetylcholine esterase inhibition and extra pyramidal syndrome: a review of neurotoxicity of organophosphate. Neurotoxicology 2001;22:423–7 - PubMed
-
- Eisenkraft A, Falk A, Finkelstein A. The role of glutamate and the immune system in organophosphate-induced CNS damage. Neurotox Res 2013;24:265–79 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
