Effects of the PPAR-α agonist fenofibrate on acute and short-term consequences of brain ischemia
- PMID: 24398933
- PMCID: PMC3948136
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.233
Effects of the PPAR-α agonist fenofibrate on acute and short-term consequences of brain ischemia
Abstract
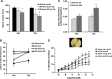
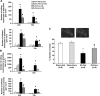
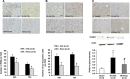
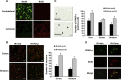
In stroke, there is an imperative need to develop disease-modifying drugs able to (1) induce neuroprotection and vasculoprotection, (2) modulate recovery and brain plasticity, and (3) limit the short-term motor and cognitive consequences. We hypothesized that fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) agonist, could exert a beneficial effect on immediate and short-term poststroke consequences related to its pleiotropic mechanisms. Rats or mice were subjected to focal ischemia to determine the effects of acute treatment by fenofibrate on (i) motor and memory impairment, (2) both cerebral and vascular compartments, (3) inflammation, (4) neurogenesis, and (5) amyloid cascade. We show that fenofibrate administration results in both neuronal and vascular protection and prevents the short-term motor and cognitive poststroke consequences by interaction with several mechanisms. Modulation of PPAR-α generates beneficial effects in the immediate poststroke consequences by mechanisms involving the interactions between polynuclear neutrophils and the vessel wall, and microglial activation. Fenofibrate modulates mechanisms involved in neurorepair and amyloid cascade. Our results suggest that PPAR-α agonists could check the key points of a potential disease-modifying effect in stroke.
Figures

References
-
- del Zoppo GJ. Stroke and neurovascular protection. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:553–555. - PubMed
-
- Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;5:347–360. - PubMed
-
- Pluta R, Ułamek M, Jablonski M. Consideration of the ischemic basis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2010;48:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Collino M, Patel NS, Thiemermann C. PPARs as new therapeutic targets for the treatment of cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2008;2:179–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

