Atrazine molecular imprinted polymers: comparative analysis by far-infrared and ultraviolet induced polymerization
- PMID: 24398982
- PMCID: PMC3907826
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15010574
Atrazine molecular imprinted polymers: comparative analysis by far-infrared and ultraviolet induced polymerization
Abstract
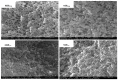
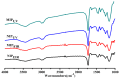
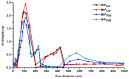
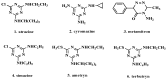
Atrazine molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) were comparatively synthesized using identical polymer formulation by far-infrared (FIR) radiation and ultraviolet (UV)-induced polymerization, respectively. Equilibrium binding experiments were carried out with the prepared MIPs; the results showed that MIP(uv) possessed specific binding to atrazine compared with their MIP(FIR) radiation counterparts. Scatchard plot's of both MIPs indicated that the affinities of the binding sites in MIPs are heterogeneous and can be approximated by two dissociation-constants corresponding to the high- and low-affinity binding sites. Moreover, several common pesticides including atrazine, cyromazine, metamitron, simazine, ametryn, terbutryn were tested to determine their specificity, similar imprinting factor (IF) and different selectivity index (SI) for both MIPs. Physical characterization of the polymers revealed that the different polymerization methods led to slight differences in polymer structures and performance by scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier transform infrared absorption (FT-IR), and mercury analyzer (MA). Finally, both MIPs were used as selective sorbents for solid phase extraction (SPE) of atrazine from lake water, followed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. Compared with commercial C18 SPE sorbent (86.4%-94.8%), higher recoveries of atrazine in spiked lake water were obtained in the range of 90.1%-97.1% and 94.4%-101.9%, for both MIPs, respectively.
Figures



References
-
- Wulff G., Sarhan A. Use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1972;11:341–342.
-
- Vlatakis G., Andersson L.I., Müller R., Mosbach K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature. 1993;361:645–647. - PubMed
-
- Claude B., Nehmé R., Morin P. Analysis of urinary neurotransmitters by capillary electrophoresis: Sensitivity enhancement using field-amplified sample injection and molecular imprinted polymer solid phase extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2011;699:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y.Q., Liu Y.H., Guo H.B., He L.M., Fang B.H., Zeng Z.L. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for determination of tilmicosin in feed using high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2011;690:269–274. - PubMed
-
- Lin Z., Yang F., He X., Zhao X., Zhang Y. Preparation and evaluation of a macroporous molecularly imprinted hybrid silica monolithic column for recognition of proteins by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2009;1216:8612–8622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

