Use of Medicare data to identify coronary heart disease outcomes in the Women's Health Initiative
- PMID: 24399330
- PMCID: PMC4548886
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.113.000373
Use of Medicare data to identify coronary heart disease outcomes in the Women's Health Initiative
Abstract
Background: Data collected as part of routine clinical practice could be used to detect cardiovascular outcomes in pragmatic clinical trials or clinical registry studies. The reliability of claims data for documenting outcomes is unknown.
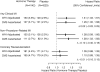
Methods and results: We linked records of Women's Health Initiative (WHI) participants aged ≥65 years to Medicare claims data and compared hospitalizations that had diagnosis codes for acute myocardial infarction or coronary revascularization with WHI outcomes adjudicated by study physicians. We then compared the hazard ratios for active versus placebo hormone therapy based solely on WHI-adjudicated events with corresponding hazard ratios based solely on claims data for the same hormone trial participants. Agreement between WHI-adjudicated outcomes and Medicare claims was good for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (κ, 0.71-0.74) and excellent for coronary revascularization (κ, 0.88-0.91). The hormone:placebo hazard ratio for clinical myocardial infarction was 1.31 (95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.67) based on WHI outcomes and 1.29 (95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.68) based on Medicare data. The hazard ratio for coronary revascularization was 1.09 (95% confidence interval, 0.88-1.35) based on WHI outcomes and 1.10 (95% confidence interval, 0.89-1.35) based on Medicare data. The differences between hazard ratios derived from WHI and Medicare data were not significant in 1000 bootstrap replications.
Conclusions: Medicare claims may provide useful data on coronary heart disease outcomes among patients aged ≥65 years in clinical research studies.
Clinical trials registration information: URL: www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00000611.
Keywords: myocardial infarction; patient outcome assessment; pragmatic clinical trials; randomized controlled trials; validation studies.
Figures
References
-
- Brennan JM, Peterson ED, Messenger JC, Rumsfeld JS, Weintraub WS, Anstrom KJ, Eisenstein EL, Milford-Beland S, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Booth ME, Dokholyan RS, Douglas PS. Linking the National Cardiovascular Data Registry CathPCI Registry with Medicare claims data: Validation of a longitudinal cohort of elderly patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs JP, Edwards FH, Shahian DM, Haan CK, Puskas JD, Morales DL, Gammie JS, Sanchez JA, Brennan JM, O'Brien SM, Dokholyan RS, Hammill BG, Curtis LH, Peterson ED, Badhwar V, George KM, Mayer JE, Chitwood WR, Murray GF, Grover FL. Successful linking of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons adult cardiac surgery database to Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Medicare data. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90:1150–1157. - PubMed
-
- Brown ML, Riley GF, Schussler N, Etzioni R. Estimating health care costs related to cancer treatment from SEER-Medicare data. Med Care. 2002;40:IV-104–117. - PubMed
-
- St Peter WL, Liu J, Weinhandl ED, Fan Q. Linking Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services data with prospective DCOR trial data: Methods and data comparison results. Hemodial Int. 2008;12:480–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD006899/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042109/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical