The ENIGMA Consortium: large-scale collaborative analyses of neuroimaging and genetic data
- PMID: 24399358
- PMCID: PMC4008818
- DOI: 10.1007/s11682-013-9269-5
The ENIGMA Consortium: large-scale collaborative analyses of neuroimaging and genetic data
Abstract
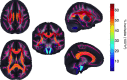
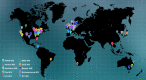
The Enhancing NeuroImaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) Consortium is a collaborative network of researchers working together on a range of large-scale studies that integrate data from 70 institutions worldwide. Organized into Working Groups that tackle questions in neuroscience, genetics, and medicine, ENIGMA studies have analyzed neuroimaging data from over 12,826 subjects. In addition, data from 12,171 individuals were provided by the CHARGE consortium for replication of findings, in a total of 24,997 subjects. By meta-analyzing results from many sites, ENIGMA has detected factors that affect the brain that no individual site could detect on its own, and that require larger numbers of subjects than any individual neuroimaging study has currently collected. ENIGMA's first project was a genome-wide association study identifying common variants in the genome associated with hippocampal volume or intracranial volume. Continuing work is exploring genetic associations with subcortical volumes (ENIGMA2) and white matter microstructure (ENIGMA-DTI). Working groups also focus on understanding how schizophrenia, bipolar illness, major depression and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affect the brain. We review the current progress of the ENIGMA Consortium, along with challenges and unexpected discoveries made on the way.
Figures


References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2013). The Worldwide ADNI. URL: http://www.alz.org/research/funding/partnerships/ww-adni_overview.asp. Accessed 2 June 2013.
-
- Amunts K, Schleicher A, Burgel U, Mohlberg H, Uylings HB, Zilles K. Broca’s region revisited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1999;412:319–341. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Andersson JL, Friston KJ. High-dimensional image registration using symmetric priors. NeuroImage. 1999;9:619–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 LM011384/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- 100309/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701120/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K01 MH099232/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0600429/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EB020407/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG040770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0802462/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K99 MH101367/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- R01 EB015611/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K99 LM011384/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- 104036/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB005846/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094524/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L016400/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EB006841/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J006742/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001245/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM011360/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

