The emerging neurobiology of calorie addiction
- PMID: 24399459
- PMCID: PMC3882917
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.01928
The emerging neurobiology of calorie addiction
Abstract
The response of the brain to sugar is determined by specific cell populations in the brain, including neurons that secrete melanin-concentrating hormone, and culminates in the release of dopamine.
Keywords: feeding behavior; metabolism; neuronal circuits; nutrient; obesity; optogenetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
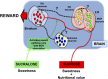
Comment on
-
Hypothalamic melanin concentrating hormone neurons communicate the nutrient value of sugar.Elife. 2013 Dec 31;2:e01462. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01462. Elife. 2013. PMID: 24381247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown AW, Bohan Brown MM, Onken KL, Beitz DC. 2011. Short-term consumption of sucralose, a nonnutritive sweetener, is similar to water with regard to select markers of hunger signaling and short-term glucose homeostasis in women. Nutrition Research 31:882–888. 10.1016/j.nutres.2011.10.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

