Structure, gene regulation and environmental response of flagella in Vibrio
- PMID: 24400002
- PMCID: PMC3872333
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00410
Structure, gene regulation and environmental response of flagella in Vibrio
Abstract
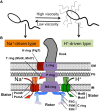
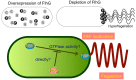
Vibrio species are Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria that live in aqueous environments. Several species, such as V. harveyi, V. alginotyticus, and V. splendidus, are associated with diseases in fish or shellfish. In addition, a few species, such as V. cholerae and V. parahaemolyticus, are risky for humans due to infections from eating raw shellfish infected with these bacteria or from exposure of wounds to the marine environment. Bacterial flagella are not essential to live in a culture medium. However, most Vibrio species are motile and have rotating flagella which allow them to move into favorable environments or to escape from unfavorable environments. This review summarizes recent studies about the flagellar structure, function, and regulation of Vibrio species, especially focused on the Na(+)-driven polar flagella that are principally responsible for motility and sensing the surrounding environment, and discusses the relationship between flagella and pathogenicity.
Keywords: bacterial flagellum; chemotaxis; ion-driven motor; motility; pathogenicity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Polar Flagellar Transcriptional Regulatory Network in Vibrio campbellii Deviates from Canonical Vibrio Species.J Bacteriol. 2021 Sep 23;203(20):e0027621. doi: 10.1128/JB.00276-21. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34339299 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio Flagellar Synthesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 May 1;9:131. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00131. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31119103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The polar flagellar motor of Vibrio cholerae is driven by an Na+ motive force.J Bacteriol. 1999 Mar;181(6):1927-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.6.1927-1930.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10074090 Free PMC article.
-
Motility of Vibrio spp.: regulation and controlling strategies.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Oct;104(19):8187-8208. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10794-7. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32816086 Review.
-
Analysis of the role of flagellar activity in virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae.Microbiology (Reading). 2001 Apr;147(Pt 4):831-837. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-4-831. Microbiology (Reading). 2001. PMID: 11283279
Cited by
-
The Vibrio H-Ring Facilitates the Outer Membrane Penetration of the Polar Sheathed Flagellum.J Bacteriol. 2018 Oct 10;200(21):e00387-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00387-18. Print 2018 Nov 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30104237 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of in vivo Essential Genes of Vibrio vulnificus for Establishment of Wound Infection by Signature-Tagged Mutagenesis.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 1;10:123. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00123. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30774628 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal Gene Transfer Clarifies Taxonomic Confusion and Promotes the Genetic Diversity and Pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides.mSystems. 2020 Sep 15;5(5):e00448-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00448-20. mSystems. 2020. PMID: 32934114 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotaxis may assist marine heterotrophic bacterial diazotrophs to find microzones suitable for N2 fixation in the pelagic ocean.ISME J. 2022 Nov;16(11):2525-2534. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01299-4. Epub 2022 Aug 1. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 35915168 Free PMC article.
-
ArgR regulates motility and virulence through positive control of flagellar genes and inhibition of diguanylate cyclase expression in Aeromonas veronii.Commun Biol. 2024 Dec 31;7(1):1720. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07392-y. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39741221 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

