Competition for zinc binding in the host-pathogen interaction
- PMID: 24400228
- PMCID: PMC3872050
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00108
Competition for zinc binding in the host-pathogen interaction
Abstract
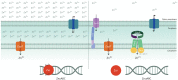
Due to its favorable chemical properties, zinc is used as a structural or catalytic cofactor in a very large number of proteins. Despite the apparent abundance of this metal in all cell types, the intracellular pool of loosely bound zinc ions available for biological exchanges is in the picomolar range and nearly all zinc is tightly bound to proteins. In addition, to limit bacterial growth, some zinc-sequestering proteins are produced by eukaryotic hosts in response to infections. Therefore, to grow and multiply in the infected host, bacterial pathogens must produce high affinity zinc importers, such as the ZnuABC transporter which is present in most Gram-negative bacteria. Studies carried in different bacterial species have established that disruption of ZnuABC is usually associated with a remarkable loss of pathogenicity. The critical involvement of zinc in a plethora of metabolic and virulence pathways and the presence of very low number of zinc importers in most bacterial species mark zinc homeostasis as a very promising target for the development of novel antimicrobial strategies.
Keywords: Salmonella enterica; ZnuABC; antibacterial therapies; host-pathogen interaction; metal cofactor; nutritional immunity; zinc transporter; zinc uptake.
Figures
References
-
- Ammendola S., Pasquali P., Pistoia C., Petrucci P., Petrarca P., Rotilio G., et al. (2007). High-affinity Zn2+ uptake system ZnuABC is required for bacterial zinc homeostasis in intracellular environments and contributes to the virulence of Salmonella enterica. Infect. Immun. 75, 5867–5876 10.1128/IAI.00559-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

