A single vector-based strategy for marker-less gene replacement in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- PMID: 24401024
- PMCID: PMC3893515
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-4
A single vector-based strategy for marker-less gene replacement in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
Background: The cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 is widely used for research on photosynthesis and circadian rhythms, and also finds application in sustainable biotechnologies. Synechocystis is naturally transformable and undergoes homologous recombination, which enables the development of a variety of tools for genetic and genomic manipulations. To generate multiple gene deletions and/or replacements, marker-less manipulation methods based on counter-selection are generally employed. Currently available methods require two transformation steps with different DNA plasmids.
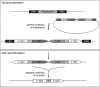
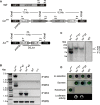
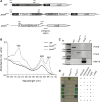
Results: In this study, we present a marker-less gene deletion and replacement strategy in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 which needs only a single transformation step. The method utilizes an nptI-sacB double selection cassette and exploits the ability of the cyanobacterium to undergo two successive genomic recombination events via double and single crossing-over upon application of appropriate selective procedures.
Conclusions: By reducing the number of cloning steps, this strategy will facilitate gene manipulation, gain-of-function studies, and automated screening of mutants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Engineering of Cyanobacteria: Design, Implementation, and Characterization of Recombinant Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1927:139-154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9142-6_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30788790
-
Construction of gene interruptions and gene deletions in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;684:295-312. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-925-3_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20960137
-
A novel counter-selection method for markerless genetic modification in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Biotechnol Prog. 2013 Jan-Feb;29(1):23-30. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1661. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Biotechnol Prog. 2013. PMID: 23124993
-
Development of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 as a phototrophic cell factory.Mar Drugs. 2013 Aug 13;11(8):2894-916. doi: 10.3390/md11082894. Mar Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23945601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current knowledge and recent advances in understanding metabolism of the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20193325. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193325. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32149336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic, Genomics, and Responses to Stresses in Cyanobacteria: Biotechnological Implications.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;12(4):500. doi: 10.3390/genes12040500. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synechocystis: Not Just a Plug-Bug for CO2, but a Green E. coli.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Sep 18;2:36. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00036. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25279375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyanobacteria as an Experimental Platform for Modifying Bacterial and Plant Photosynthesis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Apr 21;2:7. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00007. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25024050 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extracellular CahB1 from Sodalinema gerasimenkoae IPPAS B-353 Acts as a Functional Carboxysomal β-Carbonic Anhydrase in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;12(2):265. doi: 10.3390/plants12020265. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678979 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Engineering, Synthetic Biology and the Light Reactions of Photosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 2019 Mar;179(3):778-793. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00360. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 29991483 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whatley JM, Whatley FR. Chloroplast evolution. New Phytol. 1981;87:233. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1981.tb03195.x. - DOI
-
- Kaneko T, Sato S, Kotani H, Tanaka A, Asamizu E, Nakamura Y, Miyajima N, Hirosawa M, Sugiura M, Sasamoto S. et al.Sequence analysis of the genome of the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. II. Sequence determination of the entire genome and assignment of potential protein-coding regions (supplement) DNA Res. 1996;3:185–209. doi: 10.1093/dnares/3.3.185. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

