The laparoscopic hiatoplasty with antireflux surgery is a safe and effective procedure to repair giant hiatal hernia
- PMID: 24401085
- PMCID: PMC3898021
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2482-14-1
The laparoscopic hiatoplasty with antireflux surgery is a safe and effective procedure to repair giant hiatal hernia
Abstract
Background: Although minimally invasive repair of giant hiatal hernias is a very surgical challenge which requires advanced laparoscopic learning curve, several reports showed that is a safe and effective procedure, with lower morbidity than open approach. In the present study we show the outcomes of 13 patients who underwent a laparoscopic repair of giant hiatal hernia.
Methods: A total of 13 patients underwent laparoscopic posterior hiatoplasty and Nissen fundoplication. Follow-up evaluation was done clinically at intervals of 3, 6 and 12 months after surgery using the Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Health-Related Quality of Life scale, a barium swallow study, an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, an oesophageal manometry, a combined ambulatory 24-h multichannel impedance pH and bilirubin monitoring. Anatomic recurrence was defined as any evidence of gastric herniation above the diaphragmatic edge.
Results: There were no intraoperative complications and no conversions to open technique. Symptomatic GORD-HQL outcomes demonstrated a statistical significant decrease of mean value equal to 3.2 compare to 37.4 of preoperative assessment (p < 0.0001). Combined 24-h multichannel impedance pH and bilirubin monitoring after 12 months did not show any evidence of pathological acid or non acid reflux.
Conclusion: All patients were satisfied of procedure and no hernia recurrence was recorded in the study group, treated respecting several crucial surgical principles, e.g., complete sac excision, appropriate crural closure, also with direct hiatal defect where possible, and routine use of antireflux procedure.
Figures
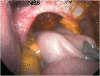
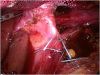


References
-
- Buenaventura PO, Schauer PR, Keenan RJ, Luketich JD. Laparoscopic repair of giant paraesophageal hernia. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;12(3):179–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

