Videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction
- PMID: 24401140
- PMCID: PMC3935461
- DOI: 10.1089/lap.2013.0172
Videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction
Abstract
Purpose: Single-incision videoendoscopic surgery has recently become popular as a result of the ongoing search for less invasive procedures. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of endoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy, axillary lymphadenectomy, and immediate reconstruction in patients with breast cancer.
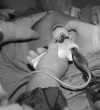
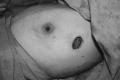
Patients and methods: From May 14, 2012 through January 23, 2013, 10 patients underwent videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and axillary dissection via a single, limited incision and immediate prosthetic reconstruction. Patient charts were reviewed, and demographic data, operative time, complications and pathology results were analyzed.
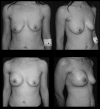
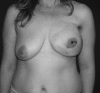
Results: In all patients, videoendoscopic surgery was performed successfully. Of 10 patients, 7 were diagnosed as having invasive ductal carcinoma, 2 had a ductal carcinoma in situ, and 1 underwent bilateral prophylactic mastectomy. The weight of the resected gland was 300-650 g, with a mean of 420 g. There were no operative complications, and the mean operative time was 250 minutes (range, 160-330 minutes). One-stage reconstruction with implants was performed on 4 patients, whereas expanders were placed in the remaining 6. Surgical margins of all cases were pathologically negative, and there were no recurrences observed during the early follow-up period.
Conclusions: Videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy is technically feasible even in larger breasts, enabling immediate reconstruction with good cosmetic outcomes. However, further studies with larger clinical series and long-term follow-up are required to compare the safety and efficacy of the technique with those of the standard nipple-sparing mastectomy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary on "videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction".J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014 Jul;24(7):506-7. doi: 10.1089/lap.2014.0065. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2014. PMID: 24905969 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010;60:277–300 - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Redmond CK, Wolmark N, Wickerham DL, Cronin WM. Reanalysis and results after 12 years of follow-up in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1456–1461 - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Salvadori B, Luini A, Greco M, Saccozzi R, del Vecchio M, et al. Breast conservation is a safe method in patients with small cancer of the breast. Long-term results of three randomised trials on 1,973 patients. Eur J Cancer 1995;31A:1574–1579 - PubMed
-
- Niemeyer M, Paepke S, Schmid R, Plattner B, Müller D, Kiechle M. Extended indications for nipple-sparing mastectomy. Breast J 2011;17:296–299 - PubMed
-
- Hinton CP, Doyle PJ, Blamey RW, Davies CJ, Holliday HW, Elston CW. Subcutaneous mastectomy for primary operable breast cancer. Br J Surg 1984;71:469–472 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

