MNK1 pathway activity maintains protein synthesis in rapalog-treated gliomas
- PMID: 24401275
- PMCID: PMC3904612
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI70198
MNK1 pathway activity maintains protein synthesis in rapalog-treated gliomas
Abstract
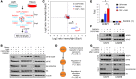
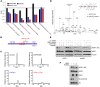
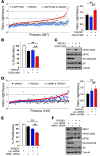
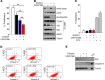
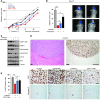
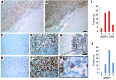
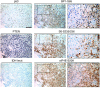
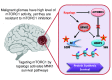
High levels of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity in malignant gliomas promote tumor progression, suggesting that targeting mTORC1 has potential as a therapeutic strategy. Remarkably, clinical trials in patients with glioma revealed that rapamycin analogs (rapalogs) have limited efficacy, indicating activation of resistance mechanisms. Targeted depletion of MAPK-interacting Ser/Thr kinase 1 (MNK1) sensitizes glioma cells to the mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin through an indistinct mechanism. Here, we analyzed how MNK1 and mTORC1 signaling pathways regulate the assembly of translation initiation complexes, using the cap analog m7GTP to enrich for initiation complexes in glioma cells followed by mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics. Association of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) with eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1) was regulated by the mTORC1 pathway, whereas pharmacological blocking of MNK activity by CGP57380 or MNK1 knockdown, along with mTORC1 inhibition by RAD001, increased 4EBP1 binding to eIF4E. Furthermore, combined MNK1 and mTORC1 inhibition profoundly inhibited 4EBP1 phosphorylation at Ser65, protein synthesis and proliferation in glioma cells, and reduced tumor growth in an orthotopic glioblastoma (GBM) mouse model. Immunohistochemical analysis of GBM samples revealed increased 4EBP1 phosphorylation. Taken together, our data indicate that rapalog-activated MNK1 signaling promotes glioma growth through regulation of 4EBP1 and indicate a molecular cross-talk between the mTORC1 and MNK1 pathways that has potential to be exploited therapeutically.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27787-801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8497. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050281 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MNK pathways enhances cancer cell response to chemotherapy with temozolomide and targeted radionuclide therapy.Cell Signal. 2016 Sep;28(9):1412-1421. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27289018
-
The androgen receptor is a negative regulator of eIF4E phosphorylation at S209: implications for the use of mTOR inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 16;36(46):6359-6373. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.233. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28745319 Free PMC article.
-
Discrete signaling mechanisms of mTORC1 and mTORC2: Connected yet apart in cellular and molecular aspects.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 May;64:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28189457 Review.
-
Lost in translation: a neglected mTOR target for lymphangioleiomyomatosis.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Sep 27;32(169):230100. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0100-2023. Print 2023 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 37758276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 (MNK1) plays as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Apr;9(4):2588-2598. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.02.67. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117618 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of inhibiting the MNK-eIF4E and PI3K/AKT/ mTOR pathways on cell migration in MDA-MB-231 cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 31;9(18):14148-14159. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24354. eCollection 2018 Mar 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29581834 Free PMC article.
-
XIAP Regulation by MNK Links MAPK and NFκB Signaling to Determine an Aggressive Breast Cancer Phenotype.Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 1;78(7):1726-1738. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1667. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29351901 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 increases CCKBR-specific tumor uptake of radiolabeled minigastrin analogue [177Lu]Lu-PP-F11N.Theranostics. 2020 Aug 29;10(24):10861-10873. doi: 10.7150/thno.45440. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 33042258 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous targeting of androgen receptor (AR) and MAPK-interacting kinases (MNKs) by novel retinamides inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cell lines.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 20;6(5):3195-210. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3084. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25605250 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

