Characterization of the biological activity of a potent small molecule Hec1 inhibitor TAI-1
- PMID: 24401611
- PMCID: PMC3895848
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-6
Characterization of the biological activity of a potent small molecule Hec1 inhibitor TAI-1
Abstract
Background: Hec1 (NDC80) is an integral part of the kinetochore and is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers, making it an attractive molecular target for the design of novel anticancer therapeutics. A highly potent first-in-class compound targeting Hec1, TAI-1, was identified and is characterized in this study to determine its potential as an anticancer agent for clinical utility.
Methods: The in vitro potency, cancer cell specificity, synergy activity, and markers for response of TAI-1 were evaluated with cell lines. Mechanism of action was confirmed with western blotting and immunofluorescent staining. The in vivo potency of TAI-1 was evaluated in three xenograft models in mice. Preliminary toxicity was evaluated in mice. Specificity to the target was tested with a kinase panel. Cardiac safety was evaluated with hERG assay. Clinical correlation was performed with human gene database.
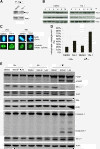
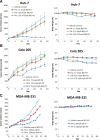
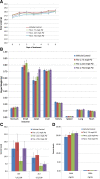
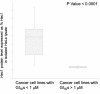
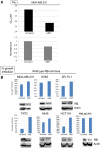
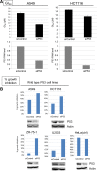
Results: TAI-1 showed strong potency across a broad spectrum of tumor cells. TAI-1 disrupted Hec1-Nek2 protein interaction, led to Nek2 degradation, induced significant chromosomal misalignment in metaphase, and induced apoptotic cell death. TAI-1 was effective orally in in vivo animal models of triple negative breast cancer, colon cancer and liver cancer. Preliminary toxicity shows no effect on the body weights, organ weights, and blood indices at efficacious doses. TAI-1 shows high specificity to cancer cells and to target and had no effect on the cardiac channel hERG. TAI-1 is synergistic with doxorubicin, topotecan and paclitaxel in leukemia, breast and liver cancer cells. Sensitivity to TAI-1 was associated with the status of RB and P53 gene. Knockdown of RB and P53 in cancer cells increased sensitivity to TAI-1. Hec1-overexpressing molecular subtypes of human lung cancer were identified.
Conclusions: The excellent potency, safety and synergistic profiles of this potent first-in-class Hec1-targeted small molecule TAI-1 show its potential for clinically utility in anti-cancer treatment regimens.
Figures
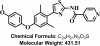


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Hec1 as a novel approach for treatment of primary liver cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;74(3):511-20. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2540-7. Epub 2014 Jul 20. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25038613
-
Activity of a novel Hec1-targeted anticancer compound against breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Jun;13(6):1419-30. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0700. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24694948
-
Discovery of T-1101 tosylate as a first-in-class clinical candidate for Hec1/Nek2 inhibition in cancer therapy.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Apr 1;191:112118. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112118. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32113126
-
Novel small molecules disrupting Hec1/Nek2 interaction ablate tumor progression by triggering Nek2 degradation through a death-trap mechanism.Oncogene. 2015 Mar 5;34(10):1220-30. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.67. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24662830 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule targeting the Hec1/Nek2 mitotic pathway suppresses tumor cell growth in culture and in animal.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 15;68(20):8393-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1915. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18922912 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Examining Nek2 as a better proliferation marker in non-small cell lung cancer prognosis.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jul;35(7):7155-62. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1935-8. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24763826
-
MAPping the Ndc80 loop in cancer: A possible link between Ndc80/Hec1 overproduction and cancer formation.Bioessays. 2015 Mar;37(3):248-56. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400175. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 25557589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of NEK2A in human cancer and its therapeutic potentials.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:862461. doi: 10.1155/2015/862461. Epub 2015 Feb 1. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25705694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of NDC80 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 28;23(20):3675-3683. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3675. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28611520 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting NEK2 as a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(7):895-907. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1152430. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27019372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

