Protein kinase G increases antioxidant function in lung microvascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the c-Abl tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 24401847
- PMCID: PMC3948974
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2012
Protein kinase G increases antioxidant function in lung microvascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the c-Abl tyrosine kinase
Abstract
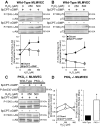
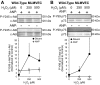
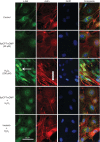
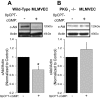
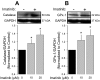
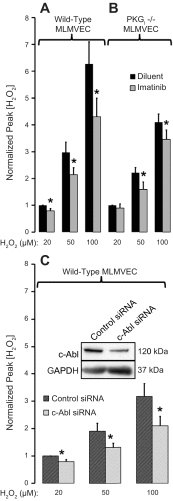
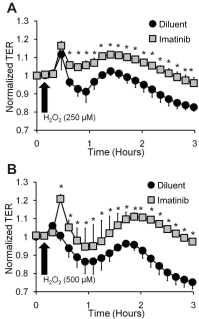
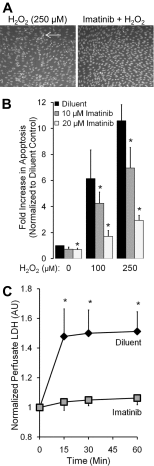
Oxidant injury contributes to acute lung injury (ALI). We previously reported that activation of protein kinase GI (PKGI) posttranscriptionally increased the key antioxidant enzymes catalase and glutathione peroxidase 1 (Gpx-1) and attenuated oxidant-induced cytotoxicity in mouse lung microvascular endothelial cells (MLMVEC). The present studies tested the hypothesis that the antioxidant effect of PKGI is mediated via inhibition of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase. We found that activation of PKGI with the cGMP analog 8pCPT-cGMP inhibited c-Abl activity and decreased c-Abl expression in wild-type but not PKGI(-/-) MLMVEC. Treatment of wild-type MLMVEC with atrial natriuretic peptide also inhibited c-Abl activation. Moreover, treatment of MLMVEC with the c-Abl inhibitor imatinib increased catalase and GPx-1 protein in a posttranscriptional fashion. In imatinib-treated MLMVEC, there was no additional effect of 8pCPT-cGMP on catalase or GPx-1. The imatinib-induced increase in antioxidant proteins was associated with an increase in extracellular H2O2 scavenging by MLMVEC, attenuation of oxidant-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction, and prevention of oxidant-induced endothelial cell death. Finally, in the isolated perfused lung, imatinib prevented oxidant-induced endothelial toxicity. We conclude that cGMP, through activation of PKGI, inhibits c-Abl, leading to increased key antioxidant enzymes and resistance to lung endothelial oxidant injury. Inhibition of c-Abl by active PKGI may be the downstream mechanism underlying PKGI-mediated antioxidant signaling. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors may represent a novel therapeutic approach in oxidant-induced ALI.
Keywords: acute lung injury; c-Abl; endothelium; oxidant injury; protein kinase G.
Figures
References
-
- Agami R, Blandino G, Oren M, Shaul Y. Interaction of c-Abl and p73alpha and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature 399: 809–813, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Akashi N, Matsumoto I, Tanaka Y, Inoue A, Yamamoto K, Umeda N, Tanaka Y, Hayashi T, Goto D, Ito S, Sekiguchi K, Sumida T. Comparative suppressive effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib in models of autoimmune arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 21: 267–275, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Aman J, van BJ, Damanafshan A, Huveneers S, Eringa EC, Vogel SM, Groeneveld AB, Vonk NA, van Hinsbergh VW, van Nieuw Amerongen GP. Effective treatment of edema and endothelial barrier dysfunction with imatinib. Circulation 126: 2728–2738, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Awazu M. Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase by atrial natriuretic peptide. Kidney Int 52: 356–362, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Brasher BB, Van Etten RA. c-Abl has high intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that is stimulated by mutation of the Src homology 3 domain and by autophosphorylation at two distinct regulatory tyrosines. J Biol Chem 275: 35631–35637, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

