Insulin resistance is associated with increased concentrations of NT-proBNP in rheumatoid arthritis: IL-6 as a potential mediator
- PMID: 24402421
- PMCID: PMC4035432
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-013-9799-4
Insulin resistance is associated with increased concentrations of NT-proBNP in rheumatoid arthritis: IL-6 as a potential mediator
Abstract
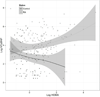
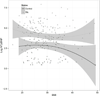
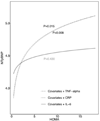
We examined the hypothesis that insulin resistance (IR) decreases circulating concentrations of N-terminal (NT)-probrain natriuretic peptide (BNP). Obesity, despite being a risk factor for heart failure (HF), is paradoxically associated with lower concentrations of BNP, a marker of myocardial stress. Low BNP in obesity is postulated to be due to IR; however, it has been difficult to define the role of IR independent of obesity. IR in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is increased, independent of obesity, thus allowing potential mechanistic insights into the relationship between IR and BNP. We measured demographic factors, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, body mass index (BMI), markers of inflammation (interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)), NT-proBNP, and IR by the homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) in 140 patients with RA and 82 control subjects. Patients with heart failure and coronary artery disease were excluded. We used multiple linear regression models to examine the relationship between HOMA and NT-proBNP in RA and controls and in RA alone, the additional effect of inflammation. As previously reported, NT-proBNP concentrations were higher in RA (median 80.49 pg/mL, IQR (23.67-167.08 pg/mL)) than controls (17.84 pg/mL (3.28-36.28 pg/mL)) (P < 0.001), and the prevalence of IR, defined by HOMA > 2.114, was higher among RA than controls (53 % vs. 15%, P > 0.001). HOMA was positively correlated with NT-proBNP (rho = 0.226, P = 0.007) in RA, but not in controls (rho = -0.154, P = 0.168). In a multivariable model adjusted for age, race, and sex, we found that increasing HOMA was statistically associated with increasing NT-proBNP concentrations in RA (P = 0.001), but not controls (P = 0.543) (P for interaction = 0.036). In RA subjects, when IL-6 was further included in the model, IL-6 (P = 0.0014), but not HOMA (P = 0.43), remained significantly associated with NT-proBNP, suggesting that IL-6 may be mechanistically involved in the relationship between IR and NT-proBNP in RA. We conclude that in patients with RA, insulin resistance is associated with higher, rather than the expected lower, concentrations of NT-proBNP and that this may be related to increased IL-6.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino-terminal fragment of the prohormone brain-type natriuretic peptide in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Sep;58(9):2662-9. doi: 10.1002/art.23796. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18759301 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and disease activity are associated with high circulating cardiac markers in rheumatoid arthritis independently of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.J Rheumatol. 2014 Feb;41(2):248-55. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.130713. Epub 2013 Dec 15. J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24334650
-
Inflammation-associated insulin resistance: differential effects in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus define potential mechanisms.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Jul;58(7):2105-12. doi: 10.1002/art.23600. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18576352 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro--B-type natriuretic peptide in the care of the vascular surgery patient.Semin Vasc Surg. 2014 Dec;27(3-4):143-7. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Semin Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 26073822 Review.
-
Association between natriuretic peptides and C-reactive protein with frailty in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Mar 6;36(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02713-x. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 38446241 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The interaction between N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and fluid status in adverse clinical outcomes of late stages of chronic kidney disease.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 22;13(8):e0202733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202733. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30133531 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of serum omentin-1 levels on cardiac prognosis in patients with heart failure.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014 Apr 23;13:84. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-84. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 24755035 Free PMC article.
-
Association of interleukin 6 and uric acid levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Bioinformation. 2022 Dec 31;18(12):1136-1140. doi: 10.6026/973206300181136. eCollection 2022. Bioinformation. 2022. PMID: 37701509 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Mediating Biomarkers underlying the Association of Body Mass Index or Waist Circumference with Blood Pressure: Results from Three Population-based Studies.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 14;7(1):5364. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05677-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28710353 Free PMC article.
-
Fatigue and interleukin-6 - a multi-faceted relationship.Reumatologia. 2015;53(4):207-12. doi: 10.5114/reum.2015.53998. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Reumatologia. 2015. PMID: 27407249 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCullough PA, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Herrmann HC, Steg PG, Duc P, Westheim A, Omland T, Knudsen CW, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Lamba S, Wu AH, Perez A, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Maisel AS. B-type natriuretic peptide and clinical judgment in emergency diagnosis of heart failure: analysis from Breathing Not Properly (BNP) multinational study. Circulation. 2002;106:416–422. - PubMed
-
- Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:161–167. - PubMed
-
- McKie PM, Rodeheffer RJ, Cataliotti A, Martin FL, Urban LH, Mahoney DW, Jacobsen SJ, Redfield MM, Burnett JC., Jr Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and B-type natriuretic peptide: biomarkers for mortality in a large community-based cohort free of heart failure. Hypertension. 2006;47:874–880. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Leip EP, Omland T, Wolf PA, Vasan RS. Plasma natriuretic peptide levels and the risk of cardiovascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:655–663. - PubMed
-
- Kistorp C, Raymond I, Pedersen F, Gustafsson F, Faber JP. Hildebrandt N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, C-reactive protein, and urinary albumin levels as predictors of mortality and cardiovascular events in older adults 2005. JAMA. 293:1609–1616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

