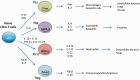
Rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology: update on emerging cytokine and cytokine-associated cell targets
- PMID: 24402580
- PMCID: PMC4135582
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket414
Rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology: update on emerging cytokine and cytokine-associated cell targets
Abstract
Biologic therapies that target pathogenic cytokines such as TNF, IL-1β or IL-6 have greatly improved the treatment of RA. Unfortunately, not all RA patients respond to current biologic therapies and responses are not always maintained, suggesting that there are alternative drivers of RA pathogenesis that might serve as promising therapeutic targets. Discovery of the new Th17 subset of Th cells, and their role in autoimmune disease development, has implicated the proinflammatory IL-12 and IL-17 families of cytokines in RA disease pathogenesis. Members of these cytokine families are elevated in the blood and joints of RA patients and have been shown to remain elevated in patients who do not respond to current biologics. In addition, these cytokines have been shown to play roles in joint destruction and erosion. A new subclass of biologics that target the IL-12 and/or IL-17 signalling pathways are under development. Here we review evidence for a role of Th17 cells as well as IL-12 and IL-17 cytokines in RA pathogenesis as the rationale for a subsequent discussion of the ongoing and completed clinical trials of newly emerging biologic therapies directed at IL-12 or IL-17 pathway inhibition.
Keywords: IL-12; IL-17; IL-17A; IL-23; Th17 cell; autoimmune disease; biologic; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; synovitis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Horton S, Walsh C, Emery P. Established rheumatoid arthritis: rationale for best practice: physicians’ perspective of how to realize tight control in clinical practice. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2011;25:509–21. - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Blanco R, Charles-Schoeman C, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:451–60. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, et al. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–57. - PubMed
-
- McInnes I, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–19. - PubMed