Efficient amide bond formation through a rapid and strong activation of carboxylic acids in a microflow reactor
- PMID: 24402801
- PMCID: PMC4499250
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201307987
Efficient amide bond formation through a rapid and strong activation of carboxylic acids in a microflow reactor
Abstract
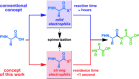
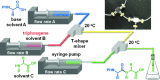
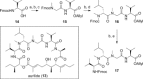
The development of highly efficient amide bond forming methods which are devoid of side reactions, including epimerization, is important, and such a method is described herein and is based on the concept of rapid and strong activation of carboxylic acids. Various carboxylic acids are rapidly (0.5 s) converted into highly active species, derived from the inexpensive and less-toxic solid triphosgene, and then rapidly (4.3 s) reacted with various amines to afford the desired peptides in high yields (74%-quant.) without significant epimerization (≤3%). Our process can be carried out at ambient temperature, and only CO2 and HCl salts of diisopropylethyl amine are generated. In the long history of peptide synthesis, a significant number of active coupling reagents have been abandoned because the highly active electrophilic species generated are usually susceptible to side reactions such as epimerization. The concept presented herein should renew interest in the use of these reagents.
Keywords: amides; amino acids; continuous flow; natural products; peptides.
Copyright © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- Yoshida J-i. Flash Chemistry—Fast Organic Synthesis in Micro Systems. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2008.
-
- Yoshida J-i, Nagaki A, Yamada T. Chem. Eur. J. 2008;14:7450–7459. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida J-i. Chem. Rec. 2010;10:332–341. - PubMed
-
- For recent reviews on the formation of amide bonds, see
-
- Han SY, Kim YA. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:2447–2467.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

