Monoubiquitination is critical for ovarian tumor domain-containing ubiquitin aldehyde binding protein 1 (Otub1) to suppress UbcH5 enzyme and stabilize p53 protein
- PMID: 24403071
- PMCID: PMC3931068
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.533109
Monoubiquitination is critical for ovarian tumor domain-containing ubiquitin aldehyde binding protein 1 (Otub1) to suppress UbcH5 enzyme and stabilize p53 protein
Abstract
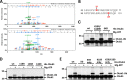
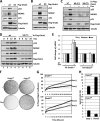
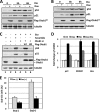
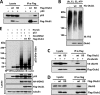
Ovarian tumor domain-containing ubiquitin (Ub) aldehyde binding protein 1 (Otub1) regulates p53 stability and activity via non-canonical inhibition of the MDM2 cognate Ub-conjugating enzyme (E2) UbcH5. However, it is not clear how this activity of Otub1 is regulated in cells. Here we report that Otub1 is monoubiquitinated by UbcH5 in cells and in vitro, primarily at the lysine 59 and 109 residues. This monoubiquitination, in turn, contributes to the activity of Otub1 to suppress UbcH5. The lysine-free Otub1 mutant (Otub1(K0)) fails to be monoubiquitinated and is unable to suppress the Ub-conjugating activity of UbcH5 in vitro and the MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination in cells. Consistently, this mutant is unable to stabilize p53, induce apoptosis, and suppress cell proliferation. Overexpression of Otub1(K0) inhibits DNA-damage induced apoptosis. Adding either Lys-59 or Lys-109 back to the Otub1(K0) mutant restores the monoubiquitination of Otub1 and its function to stabilize and activate p53. We further show that UbcH5 preferentially binds to the monoubiquitinated Otub1 via Ub interaction with its backside donor Ub-interacting surface, suggesting that this binding interferes with the self-assembly of Ub-charged UbcH5 (UbcH5∼Ub) conjugates, which is critical for Ub transfer. Thus, our data reveal novel insights into the Otub1 inhibition of E2 wherein monoubiquitination promotes the interaction of Otub1 with UbcH5 and the function to suppress it.
Keywords: Deubiquitinating Enzymes; Deubiquitination; Monoubiquitination; Otub1; UbcH5; Ubiquitin; Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme (Ubc); Ubiquitination; p53.
Figures


References
-
- Fang S., Jensen J. P., Ludwig R. L., Vousden K. H., Weissman A. M. (2000) Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein ligase for itself and p53. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8945–8951 - PubMed
-
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. (1992) The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69, 1237–1245 - PubMed
-
- Haupt Y., Maya R., Kazaz A., Oren M. (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387, 296–299 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

