Rab5 and Rab4 regulate axon elongation in the Xenopus visual system
- PMID: 24403139
- PMCID: PMC3870927
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0876-13.2014
Rab5 and Rab4 regulate axon elongation in the Xenopus visual system
Abstract
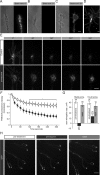
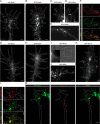
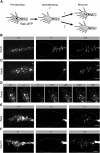
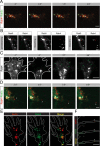
The elongation rate of axons is tightly regulated during development. Recycling of the plasma membrane is known to regulate axon extension; however, the specific molecules involved in recycling within the growth cone have not been fully characterized. Here, we investigated whether the small GTPases Rab4 and Rab5 involved in short-loop recycling regulate the extension of Xenopus retinal axons. We report that, in growth cones, Rab5 and Rab4 proteins localize to endosomes, which accumulate markers that are constitutively recycled. Fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching experiments showed that Rab5 and Rab4 are recruited to endosomes in the growth cone, suggesting that they control recycling locally. Dynamic image analysis revealed that Rab4-positive carriers can bud off from Rab5 endosomes and move to the periphery of the growth cone, suggesting that both Rab5 and Rab4 contribute to recycling within the growth cone. Inhibition of Rab4 function with dominant-negative Rab4 or Rab4 morpholino and constitutive activation of Rab5 decreases the elongation of retinal axons in vitro and in vivo, but, unexpectedly, does not disrupt axon pathfinding. Thus, Rab5- and Rab4-mediated control of endosome trafficking appears to be crucial for axon growth. Collectively, our results suggest that recycling from Rab5-positive endosomes via Rab4 occurs within the growth cone and thereby supports axon elongation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization, endosomal sorting, and plasma membrane recycling are regulated by rab GTPases.J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 1;275(35):27221-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003657200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10854436
-
Deregulation of Rab5 and Rab4 proteins in p85R274A-expressing cells alters PDGFR trafficking.Cell Signal. 2010 Oct;22(10):1562-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.05.025. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20570729
-
Rab4 affects both recycling and degradative endosomal trafficking.FEBS Lett. 2001 Apr 20;495(1-2):21-30. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02359-6. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11322941
-
Regulation of membrane transport through the endocytic pathway by rabGTPases.Mol Membr Biol. 1999 Jan-Mar;16(1):81-7. doi: 10.1080/096876899294797. Mol Membr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10332741 Review.
-
Regulation of G-protein-coupled receptor activity by rab GTPases.Recept Channels. 2002;8(2):87-97. Recept Channels. 2002. PMID: 12448790 Review.
Cited by
-
Fine-Tuning the TGFβ Signaling Pathway by SARA During Neuronal Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 3;8:550267. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.550267. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015054 Free PMC article.
-
Vps54 regulates Drosophila neuromuscular junction development and interacts genetically with Rab7 to control composition of the postsynaptic density.Biol Open. 2020 Aug 25;9(8):bio053421. doi: 10.1242/bio.053421. Biol Open. 2020. PMID: 32747448 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of SARA in Axon and Dendrite Growth.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0138792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138792. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26405814 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between the Rho and Rab family of small GTPases in neurodegenerative disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jan 27;17:1084769. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1084769. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36779014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rabs in Signaling and Embryonic Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 5;21(3):1064. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031064. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32033485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
