Performance of a redesigned HIV Selectest enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay optimized to minimize vaccine-induced seropositivity in HIV vaccine trial participants
- PMID: 24403525
- PMCID: PMC3957658
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00748-13
Performance of a redesigned HIV Selectest enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay optimized to minimize vaccine-induced seropositivity in HIV vaccine trial participants
Abstract
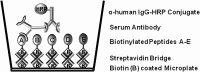
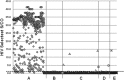
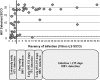
Vaccine-induced seropositivity (VISP) or seroreactivity (VISR), defined as the reaction of antibodies elicited by HIV vaccines with antigens used in HIV diagnostic immunoassays, can result in reactive assay results for vaccinated but uninfected individuals, with subsequent misclassification of their infection status. The eventual licensure of a vaccine will magnify this issue and calls for the development of mitigating solutions in advance. An immunoassay that discriminates between antibodies elicited by vaccine antigens and those elicited by infection has been developed to address this laboratory testing need. The HIV Selectest is based on consensus and clade-specific HIV peptides that are omitted in many HIV vaccine constructs. The assay was redesigned to enhance performance across worldwide clades and to simplify routine use via a standard kit format. The redesigned assay was evaluated with sera from vaccine trial participants, HIV-infected and uninfected individuals, and healthy controls. The HIV Selectest exhibited specificities of 99.5% with sera from uninfected recipients of 6 different HIV vaccines and 100% with sera from normal donors, while detecting HIV-1 infections, including intercurrent infections, with 95 to 100% sensitivity depending on the clade, with the highest sensitivities for clades A and C. HIV Selectest sensitivity decreased in very early seroconversion specimens, which possibly explains the slightly lower sensitivity observed for asymptomatic blood donors than for clinical HIV cases. Thus, the HIV Selectest provides a new laboratory tool for use in vaccine settings to distinguish the immune response to HIV vaccine antigens from that due to true infection.
Figures
References
-
- Haynes BF, Gilbert PB, McElrath MJ, Zolla-Pazner S, Tomaras GD, Alam SM, Evans DT, Montefiori DC, Karnasuta C, Sutthent R, Liao H-X, DeVico AL, Lewis GK, Williams C, Pinter A, Fong Y, Janes H, DeCamp A, Huang Y, Rao M, Billings E, Karasavvas N, Robb ML, Ngauy V, de Souza MS, Paris R, Ferrari G, Bailer RT, Soderberg KA, Andrews C, Berman PW, Frahm N, De Rosa SC, Alpert MD, Yates NL, Shen X, Koup RA, Pitisuttithum P, Kaewkungwal J, Nitayaphan S, Rerks-Ngarm S, Michael NL, Kim JH. 2012. Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 366:1275–1286. 10.1056/NEJMoa1113425 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barouch DH, Liu J, Li H, Maxfield LF, Abbink P, Lynch DM, Iampietro MJ, SanMiguel A, Seaman MS, Ferrari G, Forthal DN, Ourmanov I, Hirsch VM, Carville A, Mansfield KG, Stablein D, Pau MG, Schuitemaker H, Sadoff JC, Billings EA, Rao M, Robb ML, Kim JH, Marovich MA, Goudsmit J, Michael NL. 2012. Vaccine protection against acquisition of neutralization-resistant SIV challenges in rhesus monkeys. Nature 482:89–93. 10.1038/nature10766 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belshe RB, Clements ML, Keefer MC, Graham BS, Corey L, Sposto R, Wescott S, Lawrence D. 1994. Interpreting HIV serodiagnostic test results in the 1990s: social risks of HIV vaccine studies in uninfected volunteers. Ann. Intern. Med. 121:584–589 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

