Percutaneous Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation for humerus shaft fractures in children: A treatment concept
- PMID: 24403719
- PMCID: PMC3883241
- DOI: 10.4103/0300-1652.122375
Percutaneous Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation for humerus shaft fractures in children: A treatment concept
Abstract
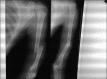
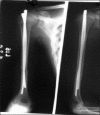
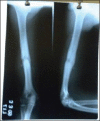
Background: Fractures of the humeral shaft are uncommon, representing less than 10 percent of all fractures in children. Humeral shaft fractures in children can be treated by immobilisation alone. A small number of fractures are unable to be reduced adequately or maintained in adequate alignment, and these should be treated surgically. In the present study, Kirschner wires (K-wire) were used to achieve a closed intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of intramedullary K-wires for the treatment of humeral shaft fracture in children.
Patients and methods: This prospective study was conducted in the Department of Orthopaedic surgery in M. M. Medical College from June 2005 to June 2010. Sixty-eight children with a mean age of 7.7 years (range, 2-14 years) were recruited from Emergency and out patient department having closed fracture of humerus shaft. All patients were operated under general anaesthesia. All patients were followed for 12 months.
Results: Out of 68 patients, 64 patients underwent union in 42-70 days with a mean of 56 days. Complications found in four patients who had insignificant delayed union which were united next 3 weeks. Intramedullary K-wires were removed after an average of 5 months without any complications. The results were excellent in 94.11% and good in 5% children.
Conclusion: This technique is simple, quick to perform, safe and reliable and avoids prolonged hospitalization with good results and is economical.
Keywords: Children; humerus shaft fractures; percutaneous Kirschner wires.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fracture union in percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation in paediatric tibial shaft fractures.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Dec 1;19(6):353-357. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.08.003. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 28088941 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous k-wire fixation for femur shaft fractures in children: a treatment concepts for developing countries.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2013 Apr;3(2):197-201. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.113661. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2013. PMID: 23919189 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of the Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures by Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation With Multiple Intramedullary Kirschner Wires (K-wires).Cureus. 2023 Dec 23;15(12):e51009. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51009. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38143728 Free PMC article.
-
[Failure of the primary treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures in children].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81(1):57-62. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014. PMID: 24755058 Czech.
-
Percutaneous pinning for treating distal radial fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 7;2(2):CD006080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006080.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32032439 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Displaced humeral shaft fractures in children and adolescents: results and adverse effects in patients treated by elastic stable intramedullary nailing.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016 Jul;26(5):453-9. doi: 10.1007/s00590-016-1758-y. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 26988699
-
Crushing Consequences: A Case Report on the Rehabilitation of a Middle Phalangeal Fracture in an Industrial Incident.Cureus. 2024 Jul 6;16(7):e63965. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63965. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39104993 Free PMC article.
-
A Shift From Non-operative Care to Surgical Fixation of Pediatric Humeral Shaft Fractures Even Though Their Severity Has Not Changed.Front Pediatr. 2020 Nov 5;8:580272. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.580272. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33240832 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with Plate and Titanium Elastic Intramedullary Nail in Treating Pediatric Humeral Fracture.Orthop Surg. 2021 Apr;13(2):434-441. doi: 10.1111/os.12897. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33470058 Free PMC article.
-
Fracture union in percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation in paediatric tibial shaft fractures.Chin J Traumatol. 2016 Dec 1;19(6):353-357. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.08.003. Chin J Traumatol. 2016. PMID: 28088941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng JC, Shen WY. Limb fracture pattern in different pediatric age groups: A study of 3,350 children. J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:15–22. - PubMed
-
- El-Adl G, Mostafa MF, Khalil MA, Enan A. Titanium elastic nail fixation for paediatric femoral and tibial fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2009;75:512–20. - PubMed
-
- Helenius I, Lamberg TS, Kääriäinen S, Impinen A, Pakarinen MP. Operative treatment of fractures in children is increasing. A population-based study from Finland. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:2612–6. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Stabile KJ, Shilt JS. Biomechanical analysis of titanium elastic nail fixation in a pediatric femur fracture model. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28:874–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources