Development and characterization of a gastroretentive dosage form composed of chitosan and hydroxyethyl cellulose for alendronate
- PMID: 24403821
- PMCID: PMC3883582
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S52791
Development and characterization of a gastroretentive dosage form composed of chitosan and hydroxyethyl cellulose for alendronate
Abstract
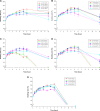
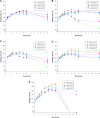
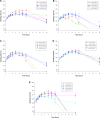
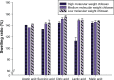
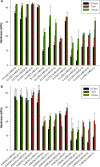
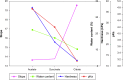
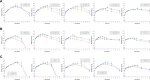
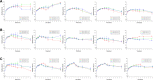
In this study, alendronate, the most commonly used biphosphonate for treating osteoporosis, was formulated as gastroretentive dosage form (GRDF) tablets to enhance its oral bioavailability. GRDF tablets were characterized with the effects of different molecular weights (MWs) of chitosan (CS) and hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) at various ratios on swelling, floating, and physical integrity. The CS component was formed using various acids: acetic, lactic, malic, succinic, and citric, and a high viscosity grade of HEC was selected. The results demonstrated that the swelling ratios of the formulations comprising high MW CS were lower than those of low or medium MW CS when salts were formed with any countering acids except for acetic acid. The decreasing ranking of the swelling rates was: CS-citrate > CS-malate > CS-lactate > CS-succinate > CS-acetate. A negative correlation was found between the pKa of the respective countering acid and the swelling rate. The swelling rate was promoted if an acidic salt of CS with a lower water content was incorporated, while it became slower when tablet hardness was higher or the compression force to form tablets was increased. Although HEC did not contribute to swelling or floating, it played a role in maintaining structural integrity. A prolonged dissolution profile of alendronate GRDF tablets developed in this study was observed.
Keywords: alendronate; chitosan; gastroretentive dosage form; hydrogel; hydroxyethyl cellulose; swelling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical characterizations and sustained release profiling of gastroretentive drug delivery systems with improved floating and swelling capabilities.Int J Pharm. 2013 Jan 30;441(1-2):162-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23237874
-
Swelling/floating capability and drug release characterizations of gastroretentive drug delivery system based on a combination of hydroxyethyl cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 24;10(1):e0116914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116914. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25617891 Free PMC article.
-
Development of swelling/floating gastroretentive drug delivery system based on a combination of hydroxyethyl cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for Losartan and its clinical relevance in healthy volunteers with CYP2C9 polymorphism.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010 Jan 31;39(1-3):82-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2009.10.015. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 19903527
-
[Development of a novel transdermal delivery system of alendronate, a nitrogen containing bisphosphonate, using a new type of hydrophilic patch and dissolving microneedle arrays].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014;134(3):427-31. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00239. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24584024 Review. Japanese.
-
Alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis in men.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008 Feb;9(3):491-8. doi: 10.1517/14656566.9.3.491. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008. PMID: 18220499 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Chitosan Swelling Behaviour on Controlled Release of Tenofovir from Mucoadhesive Vaginal Systems for Prevention of Sexual Transmission of HIV.Mar Drugs. 2017 Feb 21;15(2):50. doi: 10.3390/md15020050. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28230790 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Chitosan in Surgical and Post-Surgical Materials.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jun 15;20(6):396. doi: 10.3390/md20060396. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Development of Gastro-retentive Drug Delivery System for Trazodone Hydrochloride: a Promising Alternative to Innovator's Controlled-Release Tablet.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Sep 7;23(7):251. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02404-8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 36071254
-
Formulation and in vitro evaluation of a fast-disintegrating/sustained dual release bucoadhesive bilayer tablet of captopril for treatment of hypertension crises.Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Jul;11(4):274-83. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.189284. Res Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27651807 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric Excipients in the Technology of Floating Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 12;14(12):2779. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122779. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Streubel A, Siepmann J, Bodmeier R. Drug delivery to the upper small intestine window using gastroretentive technologies. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6(5):501–508. - PubMed
-
- Nayak AK, Maji R, Das B. Gastroretentive drug delivery systems: a review. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research. 2010;3(1):2–10.
-
- Hoffman A. Pharmacodynamic aspects of sustained release preparations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1998;33(3):185–199. - PubMed
-
- Chawla G, Gupta P, Koradia V, Bansal AK. A means to address regional variability in intestinal drug absorption. Pharmaceutical Technology. 2003;27(7):50–68.
-
- Waterman KC. A critical review of gastric retentive controlled drug delivery. Pharm Dev Technol. 2007;12(1):1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

