Incidence and risk of developing contrast-induced acute kidney injury following intravascular contrast administration in elderly patients
- PMID: 24403826
- PMCID: PMC3883550
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S55157
Incidence and risk of developing contrast-induced acute kidney injury following intravascular contrast administration in elderly patients
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the epidemiology of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) in the elderly.
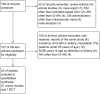
Methods: A literature review was undertaken to determine the incidence of CI-AKI in individuals receiving intravascular contrast medium in the hospital setting.
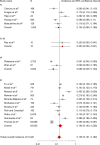
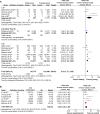
Results: Twenty-two studies with 186,455 patients were identified. The pooled incidence of CI-AKI was 13.6% in 67,831 patients older than 65 years of age (95% confidence interval [CI] 10.1-18.2, I(2) =0.496). The pooled odds ratio of CI-AKI in the elderly was 2.55 (95% CI 1.85-3.52, I(2) =0.34). The high incidence of CI-AKI in the elderly was consistent across different administration route subgroups (intracoronary contrast medium group, 15.5% [95% CI 10.3-22.6]; intravenous contrast medium group, 12.4% [95% CI 8.0-18.8]).
Conclusion: Elderly patients are at greater risk for developing CI-AKI.
Keywords: angiography; contrast-induced acute kidney injury; enhanced computed tomography; epidemiology; meta-analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Seeliger E, Sendeski M, Rihal CS, Persson PB. Contrast-induced kidney injury: mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2007–2015. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1419–1428. - PubMed
-
- Mehran R, Aymong ED, Nikolsky E, et al. A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention: development and initial validation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1393–1399. - PubMed
-
- Zhang T, Shen L, Hu L, He B. Optimal duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy following drug-eluting stent implantation: a meta-analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53:345–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

