Neurochemicals involved in medullary control of common carotid blood flow
- PMID: 24403875
- PMCID: PMC3763759
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X113119990044
Neurochemicals involved in medullary control of common carotid blood flow
Abstract
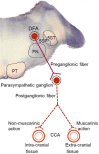
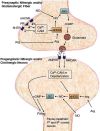
The common carotid artery (CCA) supplies intra- and extra-cranial vascular beds. An area in the medulla controlling CCA blood flow is defined as the dorsal facial area (DFA) by Kuo et al. in 1987. In the DFA, presynaptic nitrergic and/or glutamatergic fibers innervate preganglionic nitrergic and/or cholinergic neurons which give rise to the preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic 7th and 9th cranial nerves. Released glutamate from presynaptic nitrergic and/or glutamatergic fibers can activate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors on preganglionic nitrergic and/or cholinergic neurons. By modulating this glutamate release, several neurochemicals including serotonin, arginine, nitric oxide, nicotine, choline and ATP in the DFA regulate CCA blood flow. Understanding the neurochemical regulatory mechanisms can provide important insights of the physiological roles of the DFA, and may help develop therapeutic strategies for diseases involving CCA blood flow, such as migraine, hypertensive disease, Alzheimer's disease and cerebral ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Carotid artery; Cerebral blood flow; Medulla; Neurotransmitter; Parasympathetic nucleus; Vascular regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide and glutamate in the dorsal facial area regulate common carotid blood flow in the cat.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 10;594(1-3):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.020. Epub 2008 Jul 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18674532
-
P2 purinergic receptor activation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and guanylyl cyclase in the dorsal facial area of the medulla increases blood flow in the common carotid arteries of cats.Neuroscience. 2015 Feb 12;286:231-41. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.043. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25433238
-
Glutamate release upon purinergic action in the dorsal facial area of the medulla increases blood flow in the common carotid artery in cats.Neuroscience. 2009 Oct 20;163(3):898-908. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.06.048. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19559757
-
Cigarette smoking impairs nitric oxide-mediated cerebral blood flow increase: Implications for Alzheimer's disease.J Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Aug;131(4):223-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 16. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27530818 Review.
-
Cholinergic-nitrergic transmitter mechanisms in the cerebral circulation.Microsc Res Tech. 2001 Apr 15;53(2):119-28. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1076. Microsc Res Tech. 2001. PMID: 11301487 Review.
References
-
- Gonzalez G, Onofrio BM, Kerr FWL. Vasodilator system for the face. J. Neurosurg. 1975;42(6 ):696–703. - PubMed
-
- Lambert GA, Bogduk N, Goadsby PJ, Duckworth JW, Lance JW. Decreased carotid arterial resistance in cats in response to trigeminal stimulation. J. Neurosurg. 1984;61(2 ):307–315. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Lambert GA, Lance JW. Effects of locus coeruleus stimulation on carotid vascular resistance in the cat. Brain Res. 1983;278(1-2 ):175–183. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Piper RD, Lambert GA, Lance JW. Effect of stimulation of nucleus raphe dorsalis on carotid blood flow. II The cat. Am. J. Physiol. 1985;248(2 ):R263–R269. - PubMed
-
- Wang MR, Kuo JS, Chai CY. Nitric oxide produces different actions in different areas of the periaqueductal grey in cats. Neurosci. Lett. 2001;309(1 ):57–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
