A comparison of systemic inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients on regular hemodialysis
- PMID: 24403910
- PMCID: PMC3884192
- DOI: 10.1159/000355148
A comparison of systemic inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients on regular hemodialysis
Abstract
Background/aims: Systemic inflammation-based prognostic scores have prognostic power in patients with cancer, independently of tumor stage and site. Although inflammatory status is associated with mortality in hemodialysis (HD) patients, it remains to be determined as to whether these composite scores are useful in predicting clinical outcomes.
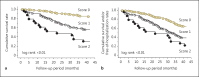
Methods: We calculated the 6 prognostic scores [Glasgow prognostic score (GPS), modified GPS (mGPS), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR), prognostic index (PI) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI), which have been established as a useful scoring system in cancer patients. We enrolled 339 patients on regular HD (age: 64 ± 13 years; time on HD: 129 ± 114 months; males/females = 253/85) and followed them for 42 months. The area under the receiver-operating characteristics curve was used to determine which scoring system was more predictive of mortality.
Results: Elevated GPS, mGPS, NLR, PLR, PI and PNI were all associated with total mortality, independent of covariates. If GPS was raised, mGPS, NLR, PLR and PI were also predictive of all-cause mortality and/or hospitalization. GPS and PNI were associated with poor nutritional status. Using overall mortality as an endpoint, the area under the curve (AUC) was significant for a GPS of 0.701 (95% CI: 0.637-0.765; p < 0.01) and for a PNI of 0.616 (95% CI: 0.553-0.768; p = 0.01). However, AUC for hypoalbuminemia (<3.5 g/dl) was comparable to that of GPS (0.695, 95% CI: 0.632-0.759; p < 0.01).
Conclusion: GPS, based on serum albumin and highly sensitive C-reactive protein, has the most prognostic power for mortality prediction among the prognostic scores in HD patients. However, as the determination of serum albumin reflects mortality similarly to GPS, other composite combinations are needed to provide additional clinical utility beyond that of albumin alone in HD patients.
Keywords: Albumin; C-reactive protein; Hemodialysis; Prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- McMillan DC. An inflammation-based prognostic score and its role in the nutrition-based management of patients with cancer. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008;67:257–262. - PubMed
-
- McMillan DC. The systematic inflammation-based Glasgow prognostic score: a decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39:534–540. - PubMed
-
- Nozoe T, Iguchi T, Egashira A, et al. Significance of modified Glasgow prognostic score as a useful indicator for prognosis of patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2011;201:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS, et al. The systematic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013;88:218–230. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

