Dynamic Changes of Treg and Th17 Cells and Related Cytokines Closely Correlate With the Virological and Biochemical Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Undergoing Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Treatment
- PMID: 24403916
- PMCID: PMC3877654
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.15332
Dynamic Changes of Treg and Th17 Cells and Related Cytokines Closely Correlate With the Virological and Biochemical Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Undergoing Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Treatment
Abstract
Background: The restoration of HBV-specific T-cell response during antiviral therapy is associated with CD4+T-cell activity. Treg cells and Th17 cells are subtypes of CD4+T cell. However, it has remained unknown how the Treg and Th17 cells and their associated cytokines affect nucleos(t)ide analogues (NA) antiviral efficacy.
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to provide a new insight to evaluate the NA antiviral therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB).
Patients and methods: Forty-four CHB patients hospitalized between July 2010 and August 2011 were enrolled in this study. They were received NA (entecavir, lamivudine and adefovir) treatment for 14.42 ± 13.08 weeks, and the peripheral blood was collected. The frequencies of Treg and Th17 cells were detected by flow cytometric analysis, and the levels of IL-10, TGF-β1, IL-17 and IL-23 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
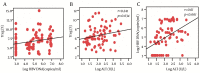
Results: In complete and partial-responders, Treg cells frequencies and IL-10, TGF-β1, IL-23 levels were all decreased significantly after NA therapy, while Th17 cells and the IL-17 levels were increased slightly. Treg/Th17 ratio was only dramatically declined in complete-responders. But there was no significant difference in non-responders. Either HBV DNA decreased by at least 2 log copies /mL or ALT turned to normal level, Treg cells frequencies and IL-10, TGF-β1, IL-23 levels were significantly reduced. Meanwhile, Treg cells were positively correlated with HBV DNA and ALT.
Conclusions: The changes of Treg and Th17 cells and their associated cytokines were related to virological and biochemical responses.
Keywords: Cytokines; Hepatitis B, Chronic; T-Lymphocytes, Regulatory; Th17 Cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes in the balance between Treg and Th17 cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Aug;76(4):437-44. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23747030
-
Ratios of regulatory T cells/T-helper 17 cells and transforming growth factor-β1/interleukin-17 to be associated with the development of hepatitis B virus-associated liver cirrhosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 May;29(5):1065-72. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12459. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24236690
-
Changes of Treg and Th17 cells balance in the development of acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 May 1;12:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-43. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22548790 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection - Dutch national guidelines.Neth J Med. 2008 Jul-Aug;66(7):292-306. Neth J Med. 2008. PMID: 18663260 Review.
-
Risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in the course of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and the protective effect of therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues.World J Hepatol. 2015 May 18;7(8):1064-73. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i8.1064. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26052395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Slow reduction of IP-10 Levels predicts HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients with 5 years of entecavir treatment.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 15;6:37015. doi: 10.1038/srep37015. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27845395 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating IL-1β, IL-17, and IP-10 as Potential Predictors of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Prognosis.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 22;2022:5202898. doi: 10.1155/2022/5202898. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35785033 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Tim-3 in hepatitis B virus infection: An overview.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 21;22(7):2294-303. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2294. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26900291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of Th17 and Treg cells at baseline for HBsAg loss in chronic hepatitis B patients with low HBsAg quantification treated with pegylated interferon and nucleos(t)ide analogue.Liver Res. 2023 May 1;7(2):136-144. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2023.04.002. eCollection 2023 Jun. Liver Res. 2023. PMID: 39958952 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Treg/Th17 balance with HBeAg change in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving telbivudine antiviral treatment: A longitudinal observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(23):e7064. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007064. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28591041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shepard CW, Simard EP, Finelli L, Fiore AE, Bell BP. Hepatitis B virus infection: epidemiology and vaccination. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28(1):112–125. - PubMed
-
- Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, Iloeje U, Veenstra DL, Kowdley KV. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38(10 Suppl 3):S158–68. - PubMed
-
- Juszczyk J, Boron-Kaczmarska A, Cianciara J, Flisiak R, Gladysz A, Halota W, et al. [Antiviral treatment of chronic B hepatitis; 2010 - therapeutic recommendations]. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2010;29(170):103–6. - PubMed
-
- Dienstag JL. Hepatitis B virus infection. New Eng J Med. 2008;359(14):1486–1500. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
