GB Virus C/Hepatitis G Virus Envelope Glycoprotein E2: Computational Molecular Features and Immunoinformatics Study
- PMID: 24403917
- PMCID: PMC3877655
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.15342
GB Virus C/Hepatitis G Virus Envelope Glycoprotein E2: Computational Molecular Features and Immunoinformatics Study
Abstract
Introduction: GB virus C (GBV-C) or hepatitis G virus (HGV) is an enveloped, RNA positive-stranded flavivirus-like particle. E2 envelope protein of GBV-C plays an important role in virus entry into the cytosol, genotyping and as a marker for diagnosing GBV-C infections. Also, there is discussion on relations between E2 protein and gp41 protein of HIV. The purposes of our study are to multi aspect molecular evaluation of GB virus C E2 protein from its characteristics, mutations, structures and antigenicity which would help to new directions for future researches.
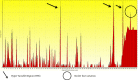
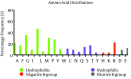
Evidence acquisition: Briefly, steps followed here were; retrieving reference sequences of E2 protein, entropy plot evaluation for finding the mutational /conservative regions, analyzing potential Glycosylation, Phosphorylation and Palmitoylation sites, prediction of primary, secondary and tertiary structures, then amino acid distributions and transmembrane topology, prediction of T and B cell epitopes, and finally visualization of epitopes and variations regions in 3D structure.
Results: Based on the entropy plot, 3 hypervariable regions (HVR) observed along E2 protein located in residues 133-135, 256-260 and 279-281. Analyzing primary structure of protein sequence revealed basic nature, instability, and low hydrophilicity of this protein. Transmembrane topology prediction showed that residues 257-270 presented outside, while residues 234- 256 and 271-293 were transmembrane regions. Just one N-glycosylation site, 5 potential phosphorylated peptides and two palmitoylation were found. Secondary structure revealed that this protein has 6 α-helix, 12 β-strand 17 Coil structures. Prediction of T-cell epitopes based on HLA-A*02:01 showed that epitope NH3-LLLDFVFVL-COOH is the best antigen icepitope. Comparative analysis for consensus B-cell epitopes regarding transmembrane topology, based on physico-chemical and machine learning approaches revealed that residue 231- 296 (NH2- EARLVPLILLLLWWWVNQLAVLGLPAVEAAVAGEVFAGPALSWCLGLPVVSMILGLANLVLYFRWL-COOH) is most effective and probable B cell epitope for E2 protein.
Conclusions: The comprehensive analysis of a protein with important roles has never been easy, and in case of E2 envelope glycoprotein of HGV, there is no much data on its molecular and immunological features, clinical significance and its pathogenic potential in hepatitis or any other GBV-C related diseases. So, results of the present study may explain some structural, physiological and immunological functions of this protein in GBV-C, as well as designing new diagnostic kits and besides, help to better understandingE2 protein characteristic and other members of Flavivirus family, especially HCV.
Keywords: GB virus C; Immunoinformatics; glycoprotein E2, GB virus C.
Figures







References
-
- Linnen J, Wages J, Jr, Zhang-Keck ZY, Fry KE, Krawczynski KZ, Alter H, et al. Molecular cloning and disease association of hepatitis G virus: a transfusion-transmissible agent. Science. 1996;271(5248):505–8. - PubMed
-
- Naito H, Abe K. Genotyping system of GBV-C/HGV type 1 to type 4 by the polymerase chain reaction using type-specific primers and geographical distribution of viral genotypes. J Virol Methods. 2001;91(1):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Fallahian F, Alavian SM, Rasoulinejad M. Epidemiology and transmission of hepatitis G virus infection in dialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010;21(5):831–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
