Celecoxib ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in type 2 diabetic rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway expression
- PMID: 24404139
- PMCID: PMC3880264
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083819
Celecoxib ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in type 2 diabetic rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway expression
Abstract
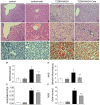
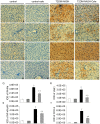
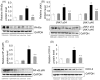
Our aim was to test whether pharmacological inhibition of cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) reverses non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway expression. Twenty-four male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly distributed to two groups and were fed with a high fat and sucrose (HF-HS) diet or a normal chow diet, respectively. After four weeks, rats fed with a HF-HS diet were made diabetic with low-dose streptozotocin. At the 9(th) week the diabetic rats fed with a HF-HS diet or the non-diabetic rats fed with a normal chow diet were further divided into two subgroups treated with vehicle or celecoxib (a selective COX-2 inhibitor, 10 mg/Kg/day, gavage) for the last 4 weeks, respectively. At the end of the 12(th) week, rats were anesthetized. NASH was assessed by histology. Related cytokine expression was measured at both the protein and gene levels through immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot and real-time PCR. T2DM rats fed with a HF-HS diet developed steatohepatitis and insulin resistance associated with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), insulin levels and the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score (NAS). The expression of Wnt5a, JNK1, NF-κB p65, and COX-2 were all significantly increased in the T2DM-NASH group compared with the control and control-cele group. Hepatic injury was improved by celecoxib in T2DM-NASH-Cele group indicated by reduced serum ALT and AST levels and hepatic inflammation was reduced by celecoxib showed by histology and the NAFLD activity score (NAS). Serum related metabolic parameters, HOMA-IR and insulin sensitivity index were all improved by celecoxib. The expression of Wnt5a, JNK1, NF-κB p65, and COX-2 expression were all suppressed by celecoxib in T2DM-NASH-Cele group. The results of the present study indicated that celecoxib ameliorated NASH in T2DM rats via suppression of the non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK1 signaling pathway expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
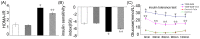
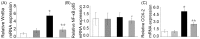
Similar articles
-
[Non-canonical Wnt signaling contributes to development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2013 Jul;21(7):537-42. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2013.07.015. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24074715 Chinese.
-
Celecoxib attenuates liver steatosis and inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis induced by high-fat diet in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2011 Sep-Oct;4(5):811-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.501. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Mol Med Rep. 2011. PMID: 21643627
-
[Effects of celecoxib on expression of PPARγ and NF-κB in type 2 diabetes rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Aug 20;24(8):590-595. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.08.007. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27788706 Chinese.
-
Role of liver parameters in diabetes mellitus - a narrative review.Endocr Regul. 2023 Sep 16;57(1):200-220. doi: 10.2478/enr-2023-0024. Print 2023 Jan 1. Endocr Regul. 2023. PMID: 37715985 Review.
-
Insulin resistance and neurodegeneration: roles of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Oct;10(10):1049-60. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19777393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Fibrosis for Drug Options: An Update.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Dec 28;9(6):960-971. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00065. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34966659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential response of rat strains to obesogenic diets underlines the importance of genetic makeup of an individual towards obesity.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09149-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831087 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of non-canonical Wnt ligands and oxidative glucose metabolism in NASH induced by methionine-choline deficient diet.Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2018;13:47-56. Trends Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30853754 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib attenuates hepatosteatosis by impairing de novo lipogenesis via Akt-dependent lipogenic pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(14):3995-4006. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17435. Epub 2022 Jun 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35713152 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Inulin Supplementation Alters Hepatic DNA Methylation Profile and Improves Glucose Metabolism in Offspring Mice.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 7;11:70. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00070. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32116778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M (2010) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease from pathogenesis to management: an update. Obes Rev 11: 430–45. - PubMed
-
- Clark JM (2006) The epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. J Clin Gastroenterol 40 Suppl 1: S5–10. - PubMed
-
- Lo L, McLennan SV, Williams PF, Bonner J, Chowdhury S, et al. (2011) Diabetes is a progression factor for hepatic fibrosis in high fat fed mouse obesity model of non-alcoholicsteatohepatitis. J Hepatol 55: 435–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

