Silymarin induces insulin resistance through an increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog in Wistar rats
- PMID: 24404172
- PMCID: PMC3880317
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084550
Silymarin induces insulin resistance through an increase of phosphatase and tensin homolog in Wistar rats
Abstract
Background and aims: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a phosphoinositide phosphatase that regulates crucial cellular functions, including insulin signaling, lipid and glucose metabolism, as well as survival and apoptosis. Silymarin is the active ingredient in milk thistle and exerts numerous effects through the activation of PTEN. However, the effect of silymarin on the development of insulin resistance remains unknown.
Methods: Wistar rats fed fructose-rich chow or normal chow were administered oral silymarin to identify the development of insulin resistance using the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemic- euglycemic clamping. Changes in PTEN expression in skeletal muscle and liver were compared using western blotting analysis. Further investigation was performed in L6 cells to check the expression of PTEN and insulin-related signals. PTEN deletion in L6 cells was achieved by small interfering ribonucleic acid transfection.
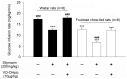
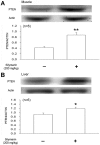
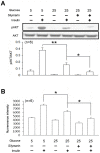
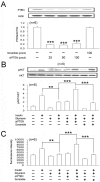
Results: Oral administration of silymarin at a dose of 200 mg/kg once daily induced insulin resistance in normal rats and enhanced insulin resistance in fructose-rich chow-fed rats. An increase of PTEN expression was observed in the skeletal muscle and liver of rats with insulin resistance. A decrease in the phosphorylation of Akt in L6 myotube cells, which was maintained in a high-glucose condition, was also observed. Treatment with silymarin aggravated high-glucose-induced insulin resistance. Deletion of PTEN in L6 cells reversed silymarin-induced impaired insulin signaling and glucose uptake.
Conclusions: Silymarin has the ability to disrupt insulin signaling through increased PTEN expression. Therefore, silymarin should be used carefully in type-2 diabetic patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Contos MJ, Choudhury J, Mills AS, Sanyal AJ (2004) The histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 8: 481–500. - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G, Babini M (2006) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome. Minerva Cardioangiol 54: 229–239. - PubMed
-
- Williams R (2006) Global challenges in liver disease. Hepatology 44: 521–526. - PubMed
-
- Flora K, Hahn M, Rosen H, Benner K (1998) Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 93: 139–143. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs BP, Dennehy C, Ramirez G, Sapp J, Lawrence VA (2002) Milk thistle for the treatment of liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 113: 506–515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

