Accuracy of microRNA discovery pipelines in non-model organisms using closely related species genomes
- PMID: 24404190
- PMCID: PMC3880327
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084747
Accuracy of microRNA discovery pipelines in non-model organisms using closely related species genomes
Abstract
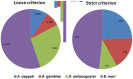
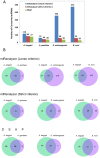
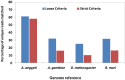
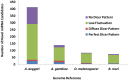
Mapping small reads to genome reference is an essential and more common approach to identify microRNAs (miRNAs) in an organism. Using closely related species genomes as proxy references can facilitate miRNA expression studies in non-model species that their genomes are not available. However, the level of error this introduces is mostly unknown, as this is the result of evolutionary distance between the proxy reference and the species of interest. To evaluate the accuracy of miRNA discovery pipelines in non-model organisms, small RNA library data from a mosquito, Aedes aegypti, were mapped to three well annotated insect genomes as proxy references using miRanalyzer with two strict and loose mapping criteria. In addition, another web-based miRNA discovery pipeline (DSAP) was used as a control for program performance. Using miRanalyzer, more than 80% reduction was observed in the number of mapped reads using strict criterion when proxy genome references were used; however, only 20% reduction was recorded for mapped reads to other species known mature miRNA datasets. Except a few changes in ranking, mapping criteria did not make any significant differences in the profile of the most abundant miRNAs in A. aegypti when its original or a proxy genome was used as reference. However, more variation was observed in miRNA ranking profile when DSAP was used as analysing tool. Overall, the results also suggested that using a proxy reference did not change the most abundant miRNAs' differential expression profiles when infected or non-infected libraries were compared. However, usage of a proxy reference could provide about 67% of the original outcome from more extremely up- or down-regulated miRNA profiles. Although using closely related species genome incurred some losses in the number of miRNAs, the most abundant miRNAs along with their differential expression profile would be acceptable based on the sensitivity level of each project.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Direct sequencing and expression analysis of a large number of miRNAs in Aedes aegypti and a multi-species survey of novel mosquito miRNAs.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 4;10:581. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-581. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19961592 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and profiling of novel microRNAs in the Brassica rapa genome based on small RNA deep sequencing.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Nov 19;12:218. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-218. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23163954 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and characterization of medaka miRNA genes by next generation sequencing platform.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 2;11 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S4-S8. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143817 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNAs expressed in two mosquito vectors, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus.BMC Genomics. 2010 Feb 18;11:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-119. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20167119 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and characterization of miRNA genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) by use of a deep sequencing approach.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 17;14:482. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-482. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23865519 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ross River Virus Provokes Differentially Expressed MicroRNA and RNA Interference Responses in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes.Viruses. 2020 Jun 27;12(7):695. doi: 10.3390/v12070695. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32605094 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel and Conserved microRNAs in Homalodisca vitripennis, the Glassy-Winged Sharpshooter by Expression Profiling.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 6;10(10):e0139771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139771. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26440407 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia-Based Approaches to Controlling Mosquito-Borne Viral Threats: Innovations, AI Integration, and Future Directions in the Context of Climate Change.Viruses. 2024 Nov 30;16(12):1868. doi: 10.3390/v16121868. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39772178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue virus infection alters post-transcriptional modification of microRNAs in the mosquito vector Aedes aegypti.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 30;5:15968. doi: 10.1038/srep15968. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26514826 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Prediction of miRNA Genes from Small RNA Sequencing Data.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Jan 26;3:7. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25674563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

