Sortilin expression is essential for pro-nerve growth factor-induced apoptosis of rat vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 24404198
- PMCID: PMC3880332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084969
Sortilin expression is essential for pro-nerve growth factor-induced apoptosis of rat vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Background: Sortilin, a member of the Vps10p-domain receptor family, has been demonstrated a key regulator in mediating cellular response to pro-neurotrophins. In the present study, we investigated the role of sortilin in the apoptotic pathway of vascular smooth muscle cells.
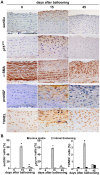
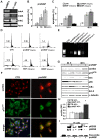
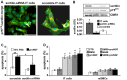
Methods and principal findings: Immunohistochemistry revealed that sortilin was barely detectable in human and rat normal young vessels, while its expression was increased in human fibroatheromatous plaques. Sortilin immunodetection was also marked in the neointima of the rat aorta fifteen days after ballooning.In vitro, rat aortic intimal cells expressed higher sortilin levels than normal media SMCs; sortilin was distributed in the cytoplasm and in correspondence of the cell membrane. After 48 h, pro-nerve growth factor (proNGF) induced the strong dose-dependent increase of intimal cell apoptosis and the accumulation of sortilin protein. ProNGF was a more potent apoptotic inducer than equimolar or even higher concentration of NGF, whereas brain derived neutrotrophic factor was ineffective. Targeted interfering RNA-mediated sortilin reduction counteracted proNGF-induced apoptosis without affecting p75(NTR) expression. ProNGF-induced apoptosis was associated to NF-κB down-regulation and bax increase. Inhibition of NF-κB activity increased intimal cell apoptosis that did not further increase with the addition of proNGF.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that sortilin expression characterizes human atheromatous lesions and rat aortic post-injury neointima, and suggest that sortilin represents an important regulator of proNGF-induced SMC apoptosis and arterial remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sortilin is expressed in cultured human keratinocytes and is regulated by cutaneous neuropeptides.J Invest Dermatol. 2010 Nov;130(11):2553-60. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.187. Epub 2010 Jul 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20613775
-
Modulation of clusterin isoforms is associated with all-trans retinoic acid-induced proliferative arrest and apoptosis of intimal smooth muscle cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Feb;25(2):348-53. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000152609.28569.e1. Epub 2004 Dec 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15591223
-
Propionyl-L-carnitine reduces proliferation and potentiates Bax-related apoptosis of aortic intimal smooth muscle cells by modulating nuclear factor-kappaB activity.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):4932-4942. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606148200. Epub 2006 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17178728
-
ProNGF, sortilin, and age-related neurodegeneration.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1119:208-15. doi: 10.1196/annals.1404.024. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056969 Review.
-
The proNGF-p75NTR-sortilin signalling complex as new target for the therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Dec;7(6):512-23. doi: 10.2174/187152708787122923. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 19128208 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and regulation of neurotrophin synthesis and secretion.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2016 Oct;21(4):306-313. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2016.4.20160080. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2016. PMID: 27744458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production and Characterization of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Against Human Sortilin.Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2015 Dec;34(6):390-5. doi: 10.1089/mab.2015.0042. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2015. PMID: 26683178 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A, cancer treatment and prevention: the new role of cellular retinol binding proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:624627. doi: 10.1155/2015/624627. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25879031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Hair Regrowth: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015 Nov;4(11):1317-23. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0107. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26400925 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hip osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: clinical and histomorphometric considerations.Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:372021. doi: 10.1155/2014/372021. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Int J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24829574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross R (1993) The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362: 801–809. - PubMed
-
- Clowes A, Reidy M, Clowes M (1983) Mechanisms of stenosis after arterial injury. Lab Invest 49: 208–215. - PubMed
-
- Isner JM, Kearney M, Bortman S, Passeri J (1995) Apoptosis in human atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circulation 91: 2703–2711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

