Evaluation of the prevalence and risk factors of delirium in cardiac surgery ICU
- PMID: 24404347
- PMCID: PMC3883539
- DOI: 10.5681/jcvtr.2013.034
Evaluation of the prevalence and risk factors of delirium in cardiac surgery ICU
Abstract
Introduction: Delirium is defined as an acute cognitive disorder presenting with fluctuation in cognition, apathy and non-organized thinking. It may increase morbidity, mortality, ICU stay and cost. In patients who underwent heart surgery delirium may increase post-operative complications such as respiratory insufficiency, sternum instability and need to re-operation of the sternum. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and risk factors of delirium in patients admitted to cardiac surgery.
Materials and methods: 18 years or older patients who had undergone cardiac surgeries and stayed for more than 24 hours in ICU following surgery were recruited. All subjects were assessed for signs & symptoms of delirium using CAM-ICU and its risk factors. All data were analyzed by SPSS 16 at the end of the study.
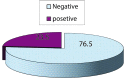
Results: The prevalence of delirium in these patients was 23.5% (47 patients). The mean age of patients with delirium was more than other patients (P=0.001). The Incidence of delirium in the patients with cardiopulmonary bypass surgery (CPB) was higher than the patients without CPB (P=0.01). The Incidence of delirium in the patients with Atrial fibrillation was higher than patients without it (P=0.002). The Incidence of delirium in the patients with CVA history was higher than the patients without CVA history (P=0.032). The mean time of mechanical ventilation in the delirious patients was more than other patients (P=0.01).
Conclusion: Older Age, CPB, history of CVA, Atrial Fibrillation, and prolonged mechanical ventilation are considered as the risk factors of delirium in cardiac surgery patients.
Keywords: Cardiac Surgery; Delirium; ICU.
References
-
- Pury BT, Wesley Ely E. The importance of diagnosing and managing ICU delirium. Chest . 2007; 132:624–636. - PubMed
-
- Devlin JW, Fong JJ, Fraser GL, Riker RR. Delirum assessment in the critically ill. Intensive care Med . 2007; 33:929–940. - PubMed
-
- Koster S, Hensens AG, Schuurmans MJ, van der Palen J. Risk factors of delirium after cardiac surgery a systemic review. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs . 2011;10:197–204. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A, Wesley Ely E, Pandharipande PP. Agitation and delirium. In: Vincent JL, Abraham E, Moore FA, Kachanek PM, Fink MP, editors. Textbook of critical care. 6th edition.Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
-
- Bucerius J, Gummert JF, Borger MA, Walther T, Doll N. Predictors of delirium after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg . 2004;127:57–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources