Toddler fearfulness is linked to individual differences in error-related negativity during preschool
- PMID: 24405180
- PMCID: PMC3889174
- DOI: 10.1080/87565641.2013.826661
Toddler fearfulness is linked to individual differences in error-related negativity during preschool
Abstract
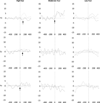
We investigated associations between early fearfulness and error-related negativity (ERN) in preschoolers. Children were classified as low, moderate, or high in fearfulness based on observations at age 2 years. ERN was measured at age 4.5 years. ERN was visible in preschoolers who were moderate or high in fear during toddlerhood, but was characterized differently in children based on associations with fearfulness during toddlerhood. A non-localized ERN was visible across midline electrodes in high-fear children and an adult like ERN distribution was visible in moderately fearful children. In contrast, low-fear children showed no evidence of ERN at 4.5 years of age.
Figures
References
-
- Bachevalier J, Mishkin M. An early and a late developing system for learning retention in infant monkeys. Behavioral Neuroscience. 1984;98:770–778. - PubMed
-
- Casey BJ, Trainor RJ, Orendi JL, Nystrom LE, Giedd JN, Castellanos FX, Haxby JV, Noll DC, Cohen JD, Forman SD, Dahl RE, Rapoport JL. A developmental functional MRI study of prefrontal activation during performance of a Go-No-Go task. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 1997;9:835–847. - PubMed
-
- Davies PL, Segalowitz SJ, Gavin WJ. Development of error-monitoring event-related potentials in adolescents. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2004;1021:324–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
