Quantitative prediction of the effect of genetic variation using hidden Markov models
- PMID: 24405700
- PMCID: PMC3893606
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-5
Quantitative prediction of the effect of genetic variation using hidden Markov models
Abstract
Background: With the development of sequencing technologies, more and more sequence variants are available for investigation. Different classes of variants in the human genome have been identified, including single nucleotide substitutions, insertion and deletion, and large structural variations such as duplications and deletions. Insertion and deletion (indel) variants comprise a major proportion of human genetic variation. However, little is known about their effects on humans. The absence of understanding is largely due to the lack of both biological data and computational resources.
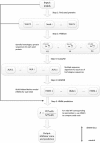
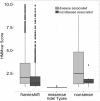
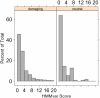
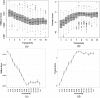
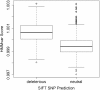
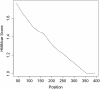
Results: This paper presents a new indel functional prediction method HMMvar based on HMM profiles, which capture the conservation information in sequences. The results demonstrate that a scoring strategy based on HMM profiles can achieve good performance in identifying deleterious or neutral variants for different data sets, and can predict the protein functional effects of both single and multiple mutations.
Conclusions: This paper proposed a quantitative prediction method, HMMvar, to predict the effect of genetic variation using hidden Markov models. The HMM based pipeline program implementing the method HMMvar is freely available at https://bioinformatics.cs.vt.edu/zhanglab/hmm.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HMMvar-func: a new method for predicting the functional outcome of genetic variants.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct 30;16:351. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0781-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26518340 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the combined effect of multiple genetic variants.Hum Genomics. 2015 Jul 30;9(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40246-015-0040-4. Hum Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26223264 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046688. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056405 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and functional impact of non-frameshifting insertion/deletion variation in the human genome.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jun 14;15(6):e1007112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007112. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31199787 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging protein structural information to improve variant effect prediction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2025 Jun;92:103023. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2025.103023. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2025. PMID: 39987793 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of small in-frame insertions/deletions in inherited eye disorders and how structural modelling can help estimate their pathogenicity.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016 Sep 14;11(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13023-016-0505-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 27628848 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Janus Associated Kinase 1 Alters Urothelial Cell Function and Facilitates the Development of Bladder Cancer.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 10;10:2065. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02065. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31552026 Free PMC article.
-
HMMvar-func: a new method for predicting the functional outcome of genetic variants.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct 30;16:351. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0781-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26518340 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and Diversification of FRUITFULL Genes in Solanaceae.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Feb 21;10:43. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00043. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30846991 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches to study the effects of small genomic variations.J Mol Model. 2015 Oct;21(10):251. doi: 10.1007/s00894-015-2794-y. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Mol Model. 2015. PMID: 26350246 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

