Cost-effectiveness of tenofovir gel in urban South Africa: model projections of HIV impact and threshold product prices
- PMID: 24405719
- PMCID: PMC3899035
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-14
Cost-effectiveness of tenofovir gel in urban South Africa: model projections of HIV impact and threshold product prices
Abstract
Background: There is urgent need for effective HIV prevention methods that women can initiate. The CAPRISA 004 trial showed that a tenofovir-based vaginal microbicide had significant impact on HIV incidence among women. This study uses the trial findings to estimate the population-level impact of the gel on HIV and HSV-2 transmission, and price thresholds at which widespread product introduction would be as cost-effective as male circumcision in urban South Africa.
Methods: The estimated 'per sex-act' HIV and HSV-2 efficacies were imputed from CAPRISA 004. A dynamic HIV/STI transmission model, parameterised and fitted to Gauteng (HIV prevalence of 16.9% in 2008), South Africa, was used to estimate the impact of gel use over 15 years. Uptake was assumed to increase linearly to 30% over 10 years, with gel use in 72% of sex-acts. Full economic programme and averted HIV treatment costs were modelled. Cost per DALY averted is estimated and a microbicide price that equalises its cost-effectiveness to that of male circumcision is estimated.
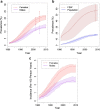
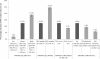
Results: Using plausible assumptions about product introduction, we predict that tenofovir gel use could lead to a 12.5% and 4.9% reduction in HIV and HSV-2 incidence respectively, by year 15. Microbicide introduction is predicted to be highly cost-effective (under $300 per DALY averted), though the dose price would need to be just $0.12 to be equally cost-effective as male circumcision. A single dose or highly effective (83% HIV efficacy per sex-act) regimen would allow for more realistic threshold prices ($0.25 and $0.33 per dose, respectively).
Conclusions: These findings show that an effective coitally-dependent microbicide could reduce HIV incidence by 12.5% in this setting, if current condom use is maintained. For microbicides to be in the range of the most cost-effective HIV prevention interventions, product costs will need to decrease substantially.
Figures
References
-
- Karim QA, Karim SS, Frohlich JA, Grobler AC, Baxter C, Mansoor LE, Kharsany AB, Sibeko S, Mlisana KP, Omar Z, Effectiveness and Safety of Tenofovir Gel, an Antiretroviral Microbicide, for the Prevention of HIV Infection in Women. Science. 2010. Epub: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/early/2010/07/19/science.1193748?expli.... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

