Escherichia coli-derived outer membrane vesicles are genotoxic to human enterocyte-like cells
- PMID: 24405746
- PMCID: PMC3898235
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-9378-9-2
Escherichia coli-derived outer membrane vesicles are genotoxic to human enterocyte-like cells
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancers are the third most common type in the world. The causes of the disease are poorly understood, but since the discovery of Helicobacter pylori as a causative agent of gastric cancer, attention has turned to bacteria as a possible trigger for colorectal cancer. Recently H. pylori outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) were revealed as potentially genotoxic which can be important first step in carcinogenesis. We therefore investigated whether OMVs from intestinal Escherichia coli could be genotoxic.
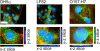
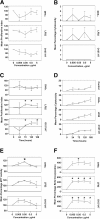
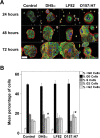
Methods: OMVs from the avirulent DH5α strain, a pathogenic adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) and an enterohaemolytic (EHEC) strain of E. coli were enriched by ultracentrifugation. The effect on the growth and viability of human enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells by OMVs was determined by trypan blue exclusion, MTT and BrdU incorporation assays. The ability of OMVs to induce DNA damage was assayed by single-cell gel electrophoresis, and 8-oxo-dG and γH2Ax immunofluorescence staining. Cytopathological changes were assessed by microscopy. The induction of aneuploidy by the OMVs was measured by flow cytometry in Caco-2 and LoVo cells.
Results: We found that OMVs derived were internalised by Caco-2 cells, increased cell numbers, induced double-stranded DNA breaks, recruited γH2Ax to the nucleus, initiated DNA rereplication, and produced distended multinucleate cells. DH5α and AIEC OMVs caused free radical generation as indicated by the reduction of glutathione in cells, leading to the development of mutagenic 8-oxo-dG adducts in DNA. Flow cytometry revealed that DH5α and EHEC OMVs increased aneuploidy in p53 mutant Caco-2 cells, but not in p53 wild type LoVo cells.
Conclusion: We conclude that E. coli derived OMVs, whether from avirulent or pathogenic strains are potentially genotoxic.
Figures
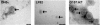


References
-
- Jemal A, Smith RA, Ward E. Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:336–378.
-
- Frizelle FA. Colorectal cancer in New Zealand. N Z Med J. 2007;120:1–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

