Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterocolitis sequentially complicated with septic arthritis: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 24405901
- PMCID: PMC3892063
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-21
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterocolitis sequentially complicated with septic arthritis: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Although most reports describing patients infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterocolitis have been published in Japan, this concept remains a matter of debate and diagnostic criteria have not yet been defined.
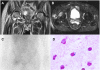
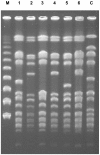
Case presentation: The general status of a 74-year-old Japanese man referred to our hospital (day 1) with severe community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia gradually improved with antibiotic therapy. Thereafter, up to 4 L/day of acute watery diarrhea that started on day 19 was refractory to metronidazole but responded immediately to oral vancomycin. Gram staining stool samples was positive for abundant fecal leukocytes from which dominant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (10(4) CFU/mL) were isolated, suggesting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterocolitis. High fever with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia was evident at day 30, and suppurative right hip arthritis developed around day 71. All methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from stools, blood and aspirated synovial fluid separated in the same manner on pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, as well as two other strains isolated from sputum, belonged to the same clone as sequence type (ST) 764 (complex clonal 5), and carried SCCmec type II.
Conclusion: The clinical, microbiological and molecular biological findings of this patient indicated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus enterocolitis that led to septic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus arthritis.
Figures


References
-
- Case definitions for infectious conditions under public health surveillance. Centers for disease control and prevention. MMWR Recomm Rep. 1997;46(RR-10):1–55. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9148133. - PubMed
-
- Multi Locus Sequence Typing home page. http://www.mlst.net/
-
- Morita H, Tani M, Adachi H, Kawai S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) enteritis associated with prophylactic cephalosporin administration and hypochlorhydria, after subtotal gastrectomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991;86(6):791–792. - PubMed
-
- Hori K, Yura J, Shinagawa N, Sakurai S, Mashita K, Mizuno A. Postoperative enterocolitis and current status of MRSA enterocolitis–the result of a questionnaire survey in Japan. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1989;63(7):701–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

