Evolution of cost structures in rheumatoid arthritis over the past decade
- PMID: 24406543
- PMCID: PMC4392312
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204311
Evolution of cost structures in rheumatoid arthritis over the past decade
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the changes in direct and indirect costs induced by patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in German rheumatology, between 2002 and 2011. To examine the impact of functional status on various cost domains. To compare the direct costs incurred by patients at working age (18-64 years) to patients at an age of retirement (≥65 years).
Methods: We analysed data from the National Database of the German Collaborative Arthritis Centres with about 3400 patients each year. Costs were calculated using fixed prices as well as annually updated cost factors. Indirect costs were calculated using the human capital as well as the friction cost approaches.
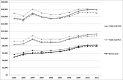
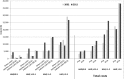
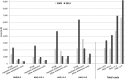
Results: There was a considerable increase in direct costs: from €4914 to €8206 in patients aged 18-64, and from €4100 to €6221 in those aged ≥65, attributable to increasing prescription of biologic agents (18-64 years from 5.6% to 31.2%, ≥65 years from 2.8% to 19.2%). This was accompanied by decreasing inpatient treatment expenses and indirect costs due to sick leave and work disability. The total growth of cost, on average, was €2437-2981 for patients at working age, and €2121 for patients at retirement age.
Conclusions: The increase in treatment costs for RA over the last decade was associated with lower hospitalisation rates, better functional status and a lower incidence of work disability, offsetting a large proportion of risen drug costs. Since the rise in drug costs has manifested a plateau from 2009 onwards, no relevant further increase in total costs for patients with RA treated in German rheumatology is expected.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); Economic Evaluations; Health services research; Outcomes research; Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modelling cost effectiveness and cost utility of sequential DMARD therapy including leflunomide in rheumatoid arthritis in Germany: I. Selected DMARDs and patient-related costs.Pharmacoeconomics. 2005;23(4):377-93. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200523040-00007. Pharmacoeconomics. 2005. PMID: 15853437
-
Costs for hospital care, drugs and lost work days in incident and prevalent rheumatoid arthritis: how large, and how are they distributed?Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Apr;74(4):648-54. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204080. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24323395
-
Burden of rheumatoid arthritis from a societal perspective: A prevalence-based study on cost of this illness for patients in China.Int J Rheum Dis. 2018 Aug;21(8):1572-1580. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13028. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 28211251
-
[Medical and economic aspects of rheumatoid arthritis].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2012 Oct;196(7):1295-305; discussion 1305-6. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2012. PMID: 23815015 Review. French.
-
Economic burden of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of literature in biologic era.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(6):771-777. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216243. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32245893
Cited by
-
Changes in referral, treatment and outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Germany in the 1990s and the 2000s.Lupus Sci Med. 2014 Dec 12;1(1):e000059. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2014-000059. eCollection 2014. Lupus Sci Med. 2014. PMID: 25553251 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Gout and Rheumatoid Arthritis Hospitalizations in Canada From 2000 to 2011.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017 May;69(5):758-762. doi: 10.1002/acr.23012. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27565008 Free PMC article.
-
Power of national economy, disease control and employment status in patients with RA-an analytical multi-site ecological study.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Feb;35(2):461-5. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2918-x. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 25805536
-
[Multimodal rheumatologic complex treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-a monocentric retrospective analysis].Z Rheumatol. 2019 Mar;78(2):136-142. doi: 10.1007/s00393-019-0593-z. Z Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30715601 German.
-
Improving patient flow of people with rheumatoid arthritis has the potential to simultaneously improve health outcomes and reduce direct costs.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jan 7;18(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1362-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28061896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Symmons D, Turner G, Webb R, et al. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:793–800. - PubMed
-
- Franke LC, Ament AJ, van de Laar MA, et al. Cost-of-illness of rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009;27:S118–23. - PubMed
-
- Kawatkar AA, Jacobsen SJ, Levy GD, et al. Direct medical expenditure associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a nationally representative sample from the medical expenditure panel survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:1649–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

